Magnetic Effects of Electric Current (विद्युत धारा के चुंबकीय प्रभाव)
Get “Magnetic Effects of Electric Current (विद्युत धारा के चुंबकीय प्रभाव)” chapter’s previous years questions from 2009 to 2020 of JAC board.
Q1. From which pole of magnet do magnetic field lines come out?
{चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ चुम्बक के किस ध्रुव से निकलती हैं?}
Ans. North pole
{उत्तर ध्रुव}
Q2. Name the device which converts electric energy to mechanical energy.
{ऐसी युक्ति का नाम बताइए जो विद्युत ऊर्जा को यांत्रिक ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित करता है|}
Ans. Electric motor
{विद्युत मोटर}
Q3. What is electromagnet?
{विद्युत चुम्बक क्या है?}
Ans. An electromagnet is a type of artificial magnet which functions on electricity.
A simple electromagnet can be created with the help of coiling of wire around a soft iron.
{विद्युत चुम्बक एक प्रकार का कृत्रिम चुम्बक है जो विद्युत पर कार्य करता है|
एक नरम लोहे के चारों ओर तार की कुंडलन की मदद से एक साधारण विद्युत चुंबक बनाया जा सकता है|}
Q4. What is a device for generating electric current called?
{विद्युत धारा उत्पन्न करने वाले युक्ति को क्या कहते हैं?}
Ans. Electric Generator
{विद्युत जनित्र}
Q5. Name a device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
{एक युक्ति का नाम बताइए जो विद्युत चुम्बकीय प्रेरण की घटना पर काम करता है|}
Ans. Electric Generator
{विद्युत जनित्र}
Q6. When does a short circuit occur in an electric circuit.
{किसी विद्युत परिपथ में लघुपथन कब होता है?}
Ans. When the neutral wire and the live wire come into direct contact due to some fault in the appliances/wire then the current flowing through the circuit abruptly increases, which occur short circuit.
{साधित्रों/तार में किसी खराबी के कारण जब विद्युत्मय तार और उदासीन तार सीधे संपर्क में आते हैं तो परिपथ में विद्युत धारा अचानक बहुत अधिक हो जाती है, जिससे लघुपथन हो जाता है|}
Q7. When is the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is largest?
{किसी चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में स्थित विद्युत धारावाही चालक पर आरोपित बल कब अधिकतम होता है?}
Ans. When the direction of electric current and magnetic field are perpendicular to each other.
{जब विद्युत धारा और चुंबकीय क्षेत्र की दिशा एक दूसरे के लंबवत होती है|}
Q8. Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
{विद्युत परिपथों और साधित्रों में सामान्यतः उपयोग किए जाने वाले दो सुरक्षा उपायों के नाम लिखिए|}
Ans. Earth wire and electric fuse.
{विद्युत फ्यूज और भूसंपर्क तार}
Q9. Name the rule by which we find the direction of force acting on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
{उस नियम का नाम लिखे जिसकी मदद से धारावाही चालक पर चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में लगने वाले बल की दिशा ज्ञात करते हैं|}
Ans. Fleming’s left hand rule
{फ्लेमिंग के वाम-हस्त नियम}
Q10. What is an electromagnet? How does a solenoid behave like a magnet?
{विद्युत चुंबक क्या है? एक परिनालिका एक चुंबक की तरह कैसे व्यवहार करती है?}
Ans. An electromagnet is a type of artificial magnet which functions on electricity.
When current passing on solenoid then one end of the solenoid acts as a north pole, while the other behaves as the south pole. The field lines inside the solenoid are arranged in the form of parallel straight lines. By which a strong magnetic field generated inside a solenoid. This magnetic field can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material (such as soft iron) when kept inside the coil and thats how solenoid behave like a magnet.
{विद्युत चुम्बक एक प्रकार का कृत्रिम चुम्बक है जो विद्युत पर कार्य करता है|
जब परिनालिका पर विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है तो परिनालिका का एक सिरा उत्तर ध्रुव और दूसरा सिरा दक्षिण ध्रुव की तरह व्यवहार करता है| परिनालिका के भीतर चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ समान्तर सरल रेखाओं की भांति होती हैं| जिससे एक परिनालिका के अंदर एक प्रबल चुंबकीय क्षेत्र उत्पन्न होता है| इस चुंबकीय क्षेत्र का उपयोग किसी चुंबकीय पदार्थ (जैसे नरम लोहे) को परिनालिका के अंदर रखकर चुम्बक बनाने में किया जा सकता है और इस तरह बने चुंबक को विद्युत चुम्बक करते है|}
Q11. Write Fleming’s left hand and right hand rule.
{फ्लेमिंग के वाम-हस्त एवं दक्षिण-हस्त नियम को लिखिए|}
Ans. Fleming’s left hand:- Stretch the fore finger, thumb and middle finger of your left hand in such a way that they are mutually perpendicular. If the first finger directs in the direction of the magnetic field and the second finger in the direction of current, then the thumb will point in the force acting on the conductor or direction of motion.
Fleming’s right hand:- Stretch the fore finger, thumb and middle finger of your right hand in such a way that they are mutually perpendicular. If the fore finger points the direction of the magnetic field and the thumb indicates the direction of motion of conductor, then the middle finger will give the direction of induced current.
{फ्लेमिंग के वाम-हस्त:- अपने बाएँ हाथ की तर्जनी, अंगूठे और मध्यमा उंगली को इस तरह फैलाएँ कि ये तीनों एक-दूसरे के आपस में लंबवत हों| यदि तर्जनी चुंबकीय क्षेत्र की दिशा में और मध्यमा चालक में प्रवाहित विद्युत धारा की दिशा की ओर संकेत करती है तो अंगूठा चालक की गति की दिशा या चालक पर आरोपित बल की दिशा की तरफ संकेत करेगा|
फ्लेमिंग के दक्षिण-हस्त:- अपने बाएँ हाथ की तर्जनी, अंगूठे और मध्यमा उंगली को इस तरह फैलाएँ कि ये तीनों एक-दूसरे के आपस में लंबवत हों| यदि तर्जनी चुंबकीय क्षेत्र की दिशा तरफ संकेत करती है और अंगूठा चालक की गति की दिशा की तरफ संकेत करता है, तो मध्यमा चालक में प्रेरित विद्युत धारा की दिशा दर्शाती है|}
Q12. Write three properties of magnetic lines of forces.
{चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाओं के तीन गुणों को लिखिए|}
Ans. (1) Magnetic field lines emerge from north pole and merge at the south pole.
(2) The direction of field lines inside the magnet is from its south pole to its north pole.
(3) No two field lines are found to cross one another.
{(1) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ चुंबक के उत्तर ध्रुव से निकलती हैं और दक्षिणी ध्रुव पर विलीन हो जाती हैं|
(2) चुंबक के अंदर क्षेत्र रेखाओं की दिशा उसके दक्षिणी ध्रुव से उसके उत्तर ध्रुव की ओर होती है|
(3) दो क्षेत्र रेखाएँ कहीं भी एक दूसरे को प्रतिच्छेद (काटती) नहीं करती|}
Q13. When does electric short circuit and overloading occur?
{किसी विद्युत परिपथ में लघुपथन और अतिभारण कब होता है?}
Ans. Overloading can take place when the neutral wire and the live wire come into direct contact. This happens when the insulation of wires is damaged or there is a fault in the appliances. In such a situation, the current flowing through the circuit abruptly increases. This is known as short circuiting. Overloading can also take place due to an accidental increase in the supply voltage. Sometimes overloading is occured by connecting too many appliances to a single socket.
{जब विद्युत्मय तार और उदासीन तार दोनों सीधे संपर्क में आते हैं तो अतिभारण हो सकता है| यह तब होता है जब तारों का विद्युतरोधन क्षतिग्रस्त हो जाता है या साधित्र में कोई दोष होता है| ऐसे अवस्थाओं में, किसी परिपथ में विद्युत धारा अचानक बहुत अधिक हो जाती है| इसे लघुपथन कहते हैं| आपूर्ति वोल्टता में दुर्घटनावश होने वाली वृद्धि से भी कभी-कभी अतिभारण हो सकता है| कभी-कभी एक ही सॉकेट में बहुत से उपकरणों को जोड़ने से भी अतिभारण हो जाता है|}
Q14. State the name of rule to determine the direction of the following:-
(a) Magnetic field produced around a straight conductor carrying current.
(b) Force experienced by a current carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
(c) Current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
निम्नलिखित की दिशा को निर्धारित करने वाले नियम का नाम बताइए:-
(a) किसी विद्युत धारावाही सीधे चालक के चारों ओर उत्पन्न चुंबकीय क्षेत्र|
(b) किसी चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में क्षेत्र के लंबवत स्थित विद्युत धारावाही सीधे चालक पर आरोपित बल|
(c) किसी चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में किसी कुण्डली के घूर्णन करने पर उस कुण्डली में उत्पन्न प्रेरित विद्युत धारा|
Ans. (a) Right hand thumb rule
(b) Fleming’s left hand rule
(c) Fleming’s right hand rule
{(a) दक्षिण-हस्त अंगुष्ठ नियम
(b) फ्लेमिंग के वाम-हस्त नियम
(c) फ्लेमिंग के दक्षिण-हस्त नियम}
Q15. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is
(a) Pushed into the coil?
(b) Withdrawn inside the coil?
(c) Held stationary inside the coil?
{कोई विद्युतरोधी ताँबे के तार की कुंडली किसी गैल्वेनोमीटर से संयोजित है| क्या होगा यदि कोई छड़ चुंबक
(a) कुंडल में धकेल जाता है?
(b) कुंडल के अंदर से बाहर खींचा जाता है?
(c) कुंडल के अंदर स्थिर रखा जाता है?}
Ans. (a) An electric current is induced in the coil and the galvanometer show a deflection.
(b) An electric current is induced in the coil but in opposite direction. The deflection of galvanometer in reverse direction.
(c) No current is induced in the coil. The galvanometer shows no deflection.
{(a) कुंडली में विद्युत धारा प्रेरित होगी और गैल्वेनोमीटर एक विक्षेप दिखाएगा|
(b) कुंडली में विद्युत धारा प्रेरित होगी लेकिन विपरीत दिशा में| गैल्वेनोमीटर का विपरीत दिशा में विक्षेपण होगा|
(c) कुण्डली में कोई धारा प्रेरित नहीं होगी| गैल्वेनोमीटर कोई विक्षेपण नहीं दिखाई देगा|}
Q16. (a) Name one source producing alternating current.
(b) What is the frequency of alternating current?
(c) Mention one main difference between alternating current and direct current.
{(a) प्रत्यावर्ती धारा उत्पन्न करने वाले एक स्रोत का नाम बताइए|
(b) प्रत्यावर्ती धारा की आवृत्ति क्या होती है?
(c) प्रत्यावर्ती धारा और दिष्ट धारा में एक मुख्य अंतर बताइए|}
Ans. (a) Generator
(b) Frequency of alternating current is equal to the number of cycles completed in 1 second.
In India, frequency of AC is 50Hz i.e, 50 cycles per second.
(c) DC current always flows in one direction, but AC current periodically reverses its direction.
{(a) जनित्र
(b) प्रत्यावर्ती धारा की आवृत्ति 1 सेकंड में पूरे किए गए चक्रों की संख्या के बराबर होती है|
भारत में प्रत्यावर्ती धारा की आवृत्ति 50Hz यानी 50 चक्र प्रति सेकेंड है|
(c) दिष्ट धारा हमेशा एक दिशा में बहती है, लेकिन प्रत्यावर्ती धारा समय-समय पर अपनी दिशा बदलती रहती है|}
Q17. The figure shows a hand diagram for Fleming’s left hand rule. Which physical quantities are represent by 1, 2 and 3 in the diagram.
{चित्र में फ्लेमिंग का वामहस्त नियम के लिए हस्त का आरेख दर्शाया गया है| चित्र 1, 2 और 3 द्वारा किन-किन भौतिक राशियों का निरूपण होता है?}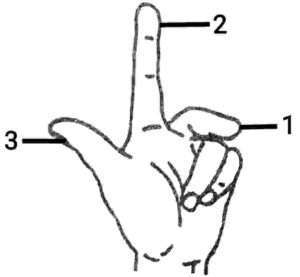
Ans. 1. Direction of current
2. Direction of magnetic field
3. Direction of motion/ Direction of force
{1. धारा की दिशा
2. चुंबकीय क्षेत्र की दिशा
3. गति की दिशा/ बल की दिशा}
Q18. When does overloading and short circuit occur in an electric circuit? What precaution should be taken to avoid the overloading and short circuit of domestic electric circuit?
{किसी विद्युत परिपथ में अतिभारण और लघुपथन कब होता है? घरेलू विद्युत परिपथों में अतिभारण और लघुपथन से बहाव के लिए क्या सावधानी बरतनी चाहिए?}
Ans. Overloading can take place when the neutral wire and the live wire come into direct contact. This happens when the insulation of wires is damaged or there is a fault in the appliances. In such a situation, the current flowing through the circuit abruptly increases. This is known as short circuiting. Overloading can also take place due to an accidental increase in the supply voltage. Sometimes overloading is occured by connecting too many appliances to a single socket.
By using electric fuse, MCB and as well as avoiding too many appliances to a single socket can avoid the overloading and short circuit of domestic electric circuits.
{जब विद्युत्मय तार और उदासीन तार दोनों सीधे संपर्क में आते हैं तो अतिभारण हो सकता है| यह तब होता है जब तारों का विद्युतरोधन क्षतिग्रस्त हो जाता है या साधित्र में कोई दोष होता है| ऐसे अवस्थाओं में, किसी परिपथ में विद्युत धारा अचानक बहुत अधिक हो जाती है| इसे लघुपथन कहते हैं| आपूर्ति वोल्टता में दुर्घटनावश होने वाली वृद्धि से भी कभी-कभी अतिभारण हो सकता है| कभी-कभी एक ही सॉकेट में बहुत से उपकरणों को जोड़ने से भी अतिभारण हो जाता है|
विद्युत फ्यूज, MCB का उपयोग करके और साथ ही एक ही सॉकेट में बहुत सारे उपकरणों का उपयोग न करके घरेलू विद्युत परिपथों में अतिभारण और लघुपथन से बचा जा सकता है|}
Q19. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
{भूसंपर्क तार का क्या कार्य है? धातु के आवरण वाले साधित्रों को भूसंपर्कित करना क्यों आवश्यक है?}
Ans. The function of an earth wire is to protect the user by any leakage of current to the metallic appliances. It is very necessary to connect metallic appliances to the earth wire such as refrigerator, table fan etc. It gives a low resistance conducting path for current. Thus, it make sure that any leakage of current to the metallic body of the appliance keeps the potential to that of the earth and the user may not get a severe electric shock.
{भूसंपर्क तार का कार्य धातु के उपकरणों में विद्युत के किसी भी क्षरण (लीक) से उपयोगकर्ता की रक्षा करना है| धातु के उपकरण को भूसंपर्क तार से जोड़ना बहुत आवश्यक है जैसे रेफ्रिजरेटर, टेबल फैन आदि| यह विद्युत धारा के लिए कम प्रतिरोध का चालन पथ प्रस्तुत करता है| इससे यह सुनिश्चित हो जाता है कि साधित्रों के धात्विक आवरण में विद्युत धारा का कोई क्षरण (लीक) होने पर इस साधित्र का विभव भूमि के विभव के बराबर हो जायेगा| फलस्वरूप इस साधित्र को उपयोग करने वाला व्यक्ति तीव्र विद्युत आघात से सुरक्षित बचा रहता है|}
Q20. What is electric motor? Describe its method of working with a diagram.
{विद्युत मोटर क्या है? इसकी कार्य-विधि का सचित्र वर्णन कीजिए|}
Ans. An electric motor is a rotating device that change electrical energy to mechanical energy.
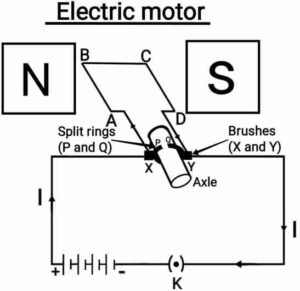 As in given figure,
As in given figure,
When current is passes through the coil ABCD then the current in arm AB of the coil flows from A to B. In arm CD it flows from C to D that is opposite to the direction of current across the arm AB. Then the force acting on arm CD pushes it upwards while the force acting on arm AB pushes it downwards. Thus the axle O and the coil, mounted free to turn about an axis, rotate anti-clockwise. At half rotation, P makes contact with the brush Y and Q with brush X. Therefore, the current in the coil gets reversed and flows across the path DCBA. The reversal of current also reverses the direction of force acting on the two arms CD and AB. Thus the arm AB is now pushed up and the arm CD is now pushed down. Therefore the axle and the coil rotate half a turn more in the same direction. The reversing of the current is repeated at each half rotation, leads to a continuous rotation of the coil and to the axle.
{विद्युत मोटर एक ऐसी घूर्णन युक्ति है जिसमें विद्युत ऊर्जा को यांत्रिक ऊर्जा में बदला जा सकता है|
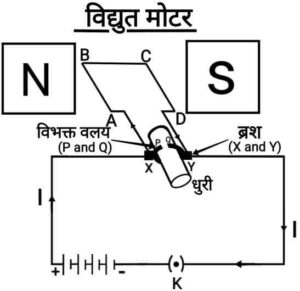 जैसा कि दिए गए चित्र में है,
जैसा कि दिए गए चित्र में है,
जब कुण्डली ABCD से धारा प्रवाहित होती है तो कुण्डली की भुजा AB में धारा A से B की ओर प्रवाहित होती है| भुजा CD में यह C से D की ओर प्रवाहित होती है जो भुजा AB पर धारा की दिशा के विपरीत होती है| फिर भुजा CD पर कार्य करने वाला बल उसे ऊपर की ओर धकेलता है जबकि भुजा AB पर कार्य करने वाला बल उसे नीचे की ओर धकेलता है| इस प्रकार किसी अक्ष पर घूमने के लिए स्वतंत्र कुंडली व धुरी वामावर्त घूर्णन करते हैं| आधे घूर्णन में Q का संपर्क ब्रश X से होता है तथा P का संपर्क ब्रश Y से होता है| इसलिए, कुंडली में विद्युत धारा उत्क्रमित होकर पथ DCBA के अनुसार प्रवाहित होती है| विद्युत धारा के पलटने पर दो भुजाओं CD और AB पर आरोपित बलों की दिशाएँ भी पलट जाती हैं| इस प्रकार कुंडली की भुजा AB अब ऊपर की ओर धकेली जाएगी और भुजा CD अब नीचे की ओर धकेली जाएगी| इसलिए कुंडली व धुरी उसी दिशा में अब आधा घूर्णन और पूरा कर लेती हैं| प्रत्येक आधे घूर्णन के बाद विद्युत धारा के उत्क्रमित होने का क्रम दोहराता रहता है जिसके परिणामस्वरूप कुंडली व धुरी का घूर्णन होता रहता है|}
Q21. Answer the following questions on the basis of the given diagram: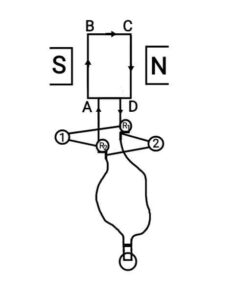 (a) Write appropriate name of the diagram .
(a) Write appropriate name of the diagram .
(b) Write the name of 1 and 2.
(c) Which type of energy is transformed through this apparatus.
(d) Write one use of this apparatus
(e) Define Armature.
{दिए गए आरेख के आधार पर निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए: (a) चित्र का उपयुक्त नाम दीजिये|
(a) चित्र का उपयुक्त नाम दीजिये|
(b) 1 और 2 के नाम लिखिए|
(c) किस प्रकार की ऊर्जा इस उपकरण के माध्यम से परिवर्तित होती है?
(d) इस उपकरण का एक उपयोग लिखिए|
(e) आर्मेचर को परिभाषित कीजिये|
Ans. (a) Electric generator
(b) Rings, Brushes
(c) Mechanical energy to electrical energy.
(d) This is used in aircraft, ships, trains.
(e) The both “coil” and “soft iron core on which the coil is wrapped” is known as an armature.
{(a) विद्युत जनित्र
(b) वलय, ब्रश
(c) यांत्रिक ऊर्जा से विद्युत ऊर्जा|
(d) इसका प्रयोग वायुयान, जहाज, रेलगाड़ियों में किया जाता है|
(e) “कुंडली” और “नर्म लौह-वेड जिसपर कुंडली को लपेटा जाता है” दोनों मिलकर आर्मेचर कहलाते हैं|}
Q22. What is electromagnetic induction? Describe an experiment to show it.
{विद्युत चुम्बकीय प्रेरण क्या है? इसे प्रदर्शित करने के लिए एक प्रयोग का वर्णन कीजिए|}
Ans. The phenomenon of generation of electric current in a conductor by changing the magnetic field around there is called electromagnetic induction.
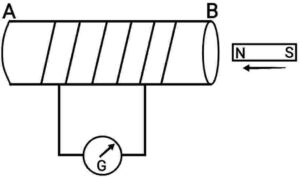 As in given figure, when we move north pole of the magnet towards the end B of the coil. There is a deflection in the needle of the galvanometer, say to the right. This shows the presence of a current in the coil AB. The deflection becomes zero when the motion of the magnet becomes stop.
As in given figure, when we move north pole of the magnet towards the end B of the coil. There is a deflection in the needle of the galvanometer, say to the right. This shows the presence of a current in the coil AB. The deflection becomes zero when the motion of the magnet becomes stop.
Now withdraw the north pole of the magnet away from the coil. Now the galvanometer get deflected towards the left, indicating that the current is now set up in the opposite direction to the first. Now, the deflection again becomes zero when the motion of the magnet becomes stop.
Similarly, when the coil is pushed towards and pulled away from the magnet, the same effects of deflections in the galvanometer are observed.
Thus, it is clear from this activity that motion of a magnet with respect to the coil or vice versa generates an induced potential difference, which sets up an induced electric current in the circuit.
{किसी चालक में उसके चारों ओर चुंबकीय क्षेत्र को बदलकर विद्युत धारा उत्पन्न करने की घटना को विद्युत चुम्बकीय प्रेरण कहा जाता है|

जैसा कि चित्र में दिया गया है, जब हम चुम्बक के उत्तर ध्रुव को कुण्डली के सिरे B की ओर ले जाते हैं| गैल्वेनोमीटर की सुई में विक्षेप होता है, मान लीजिए दाईं ओर की तरफ| यह कुण्डली AB में विद्युत धारा की उपस्थिति दर्शाता है| जैसे ही चुंबक की गति शून्य हो जाती है, गैल्वेनोमीटर में विक्षेप शून्य हो जाता है|
अब चुम्बक के उत्तर ध्रुव को कुण्डली से दूर ले जाइए| अब गैल्वेनोमीटर की सुई बाईं ओर विक्षेपित होती है, जो यह दर्शाता है कि अब परिपथ में उत्पन्न विद्युत धारा की दिशा पहले के विपरीत है| फिर चुंबक की गति शून्य होने पर, गैल्वेनोमीटर में विक्षेप फिर से शून्य हो जाता है|
इसी प्रकार, जब कुंडली को चुंबक की ओर धकेला जाता है और दूर खींचा जाता है, तो गैल्वेनोमीटर में विक्षेपण के समान प्रभाव देखे जाते हैं|
इस क्रियाकलाप से यह स्पष्ट है कि चुंबक के सापेक्ष कुंडली या कुंडली के सापेक्ष चुंबक की गति एक प्रेरित विभवांतर पैदा करती है, जिसके कारण परिपथ में प्रेरित विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है|}
Q23. (a) When does an electric short circuit occur?
(b) What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic electrical appliances?
{(a) किसी विद्युत परिपथ में लघुपथन कब होता है?
(b) भूसंपर्क तार का क्या कार्य है? धातु के आवरण वाले साधित्रों को भूसंपर्कित करना क्यों आवश्यक है?}
Ans. (a) When the neutral wire and the live wire come into direct contact, then current flowing through the circuit abruptly increases. This is known as short circuiting. This happens when the insulation of wires is damaged or there is a fault in the appliances.
(b) It is used as a safety measure, mainly for those appliances that have a metallic body, like refrigerator, electric press, table fan, toaster etc.
The metallic body is connected to the earth wire, which give a low resistance conducting path for the current. Thus, it makes sure that any leakage of current to the metallic body of the appliances keeps its potential to that of the earth and the user may not get a severe electric shock.
{(a) जब विद्युत्मय तार और उदासीन तार दोनों सीधे संपर्क में आते हैं तो परिपथ में विद्युत धारा अचानक बहुत अधिक हो जाती है| इसे लघुपथन कहते हैं| यह तब होता है जब तारों का विद्युतरोधन क्षतिग्रस्त हो जाता है या साधित्र में कोई दोष होता है|
(b) इस तार का उपयोग मुख्य रूप से रेफ्रिजरेटर, विद्युत इस्त्री, टेबल फैन, टोस्टर आदि धातु के आवरण वाले विद्युत साधित्रों में सुरक्षा के उपाय के रूप में किया जाता है|
धातु के आवरणों से जुड़े भूसंपर्क तार विद्युत धारा के लिए कम प्रतिरोध का चालन पथ प्रस्तुत करता है| इससे यह सुनिश्चित हो जाता है कि साधित्र के धात्विक आवरण में विद्युत धारा का कोई क्षरण (लीक) होने पर इस साधित्र का विभव भूमि के विभव के बारब हो जायेगा| फलस्वरूप इस साधित्र को उपयोग करने वाला व्यक्ति तीव्र विद्युत आघात से सुरक्षित बचा रहता है|
Q24. (a) What is an electric motor? Write its principle.
(b) What is the role of split ring in an electric motor?
(c) Draw a labelled diagram of motor and write its two uses.
{(a) विद्युत मोटर क्या है? इसका सिद्धांत लिखिए|
(b) विद्युत मोटर में विभक्त वलय की क्या भूमिका होती है?
(c) एक मोटर का नामांकित चित्र बनाइए और इसके दो उपयोग लिखिए|}
Ans. (a) An electric motor is a rotating device that change electrical energy to mechanical energy.
Electric motor works on the principle that when a rectangular coil is placed in a magnetic field and current is passed through it, then force acting on it which result the coil becomes rotate.
(b) In the electric motor, the role of split ring is to reverses the direction of flow of current across a circuit.
(c) 
Uses:- Fans, mixers, washing machine etc
{(a) विद्युत मोटर एक ऐसी घूर्णन युक्ति है जिसमें विद्युत ऊर्जा को यांत्रिक ऊर्जा में बदला जा सकता है|
विद्युत मोटर इस सिद्धांत पर काम करती है कि जब एक आयताकार कुंडल को चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में रखा जाता है और उसमें से विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित किया जाता है, तो उस पर बल कार्य करने लगता है जिसके परिणामस्वरूप कुंडल घूमने लगती है|
(b) विद्युत मोटर में, विभक्त वलय की भूमिका परिपथ में विद्युत के प्रवाह की दिशा को बदलना होता है|
(c) 
उपयोग:- पंखे, मिक्सर, वाशिंग मशीन आदि|
Q25. What is electromagnetic field? Prove by experiment that “When an electric current is passed through a conductor then a magnetic field is produced around it.”
{विद्युत चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र क्या है? प्रयोग द्वारा सिद्ध कीजिए कि “जब किसी चालक से विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित की जाती है, तब उसके चारों ओर चुंबकीय क्षेत्र उत्पन्न हो जाता है|”}
Ans. The region surrounding a current carrying conductor, in which the force of the magnetic field can be experienced is called electromagnetic field.
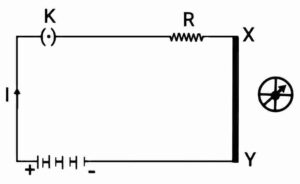 As in given figure,
As in given figure,
A straight thick copper wire is placed between the point X and Y and pass the current across the circuit. When we put a compass near to this copper wire then we observe that the needle is deflected. When we off the switch then compass comes to their normal position. It means that when an electric current is passed through a conductor then a magnetic field is produced around it.
{विद्युत धारावाही चालक के आसपास का क्षेत्र जिसमें चुंबकीय क्षेत्र के बल का अनुभव किया जा सकता है, विद्युत चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र कहलाता है|
 जैसा कि चित्र में दिया गया है,
जैसा कि चित्र में दिया गया है,
बिंदु X और Y के बीच एक सीधा मोटा ताँबे का तार रखा गया है और परिपथ में विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित किया गया है| जब हम इस ताँबे के तार के पास एक कंपास लगाते हैं तो हम देखते हैं कि सुई विक्षेपित होती है| जब हम स्विच को खोलते हैं तो कंपास अपनी सामान्य स्थिति में आ जाता है| इसका अर्थ है कि जब किसी चालक से विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित की जाती है तो उसके चारों ओर एक चुंबकीय क्षेत्र उत्पन्न हो जाता है|
Q26. Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric generator by drawing a labelled diagram. What is the function of brushes?
{नामांकित आरेख खींचकर किसी विद्युत जनित्र का मूल्य सिद्धांत तथा कार्यविधि स्पष्ट कीजिए| ब्रशों का कार्य क्या है?}
Ans. Principle:- Electric generator work on the phenomenon of “electromagnetic induction”, when a rectangular coil is rotate in a magnetic field then an electric current is induced in the coil.
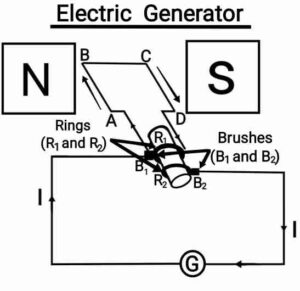 Working:- When the axel connected to the two rings are rotated in such a way that the arm AB moves up and the arm CD moves down (let us say in clockwise) in the magnetic field, then the coil intersects the magnetic fields. Then induced currents are generated in these arms along the direction AB and CD i.e, in the direction of ABCD. This shows that the current in the external circuit flows from
Working:- When the axel connected to the two rings are rotated in such a way that the arm AB moves up and the arm CD moves down (let us say in clockwise) in the magnetic field, then the coil intersects the magnetic fields. Then induced currents are generated in these arms along the direction AB and CD i.e, in the direction of ABCD. This shows that the current in the external circuit flows from to
. After half a rotation, arm AB starts moving down and CD moving up. As a result, the directions of the induced currents in both the arms change, producing the net induced current in the direction DCBA. Thus, the current in the external circuit now flows from
to
. Hence after every half rotation the polarity of the current in the respective arms changes. Thus, generator produce AC current.
Brush’s working:- 2 brushes pressed the rings separately which help to flow of current in the external circuit.
{सिद्धांत:- विद्युत जनित्र “विद्युत चुम्बकीय प्रेरण” की घटना पर काम करता है, जब एक आयताकार कुंडली को चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में घुमाया जाता है तो कुंडली में एक विद्युत धारा प्रेरित होता है|
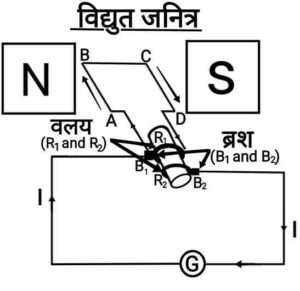 कार्यविधि:- जब दो वलयों से जुड़ी धुरी को इस तरह घुमाया जाता है कि कुंडली की भुजा AB ऊपर की ओर और भुजा CD नीचे की ओर (मान लीजिए दक्षिणावर्त में) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में गति करती है, तो कुंडली चुंबकीय क्षेत्रों को काटती है| तो इन भुजाओं में AB और CD दिशाओं के अनुदिश प्रेरित विद्युत धाराएँ प्रवाहित होने लगती हैं अर्थात ABCD की दिशा में| इसका तात्पर्य यह है कि बाह्य परिपथ में
कार्यविधि:- जब दो वलयों से जुड़ी धुरी को इस तरह घुमाया जाता है कि कुंडली की भुजा AB ऊपर की ओर और भुजा CD नीचे की ओर (मान लीजिए दक्षिणावर्त में) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में गति करती है, तो कुंडली चुंबकीय क्षेत्रों को काटती है| तो इन भुजाओं में AB और CD दिशाओं के अनुदिश प्रेरित विद्युत धाराएँ प्रवाहित होने लगती हैं अर्थात ABCD की दिशा में| इसका तात्पर्य यह है कि बाह्य परिपथ में से
की दिशा में विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है| अघूर्णन के बाद भुजा AB नीचे की ओर और CD ऊपर की ओर जाने लगती है| परिणामस्वरूप इन दोनों भुजाओं में प्रेरित विद्युत धारा की दिशा बदल जाती हैं और DCBA के अनुदिश नेट प्रेरित विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है| इस प्रकार, अब बाह्य परिपथ में
से
की दिशा में विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है| इसलिए प्रत्येक आधे घूर्णन के पश्चात क्रमित रूप से इन भुजाओं में विद्युत धारा की ध्रुवता बदलती रहती है| इस प्रकार, जनित्र AC धारा उत्पन्न करती है|
ब्रशों का कार्य:- 2 ब्रशे रिंगों को अलग-अलग दबाते है जो बाह्य परिपथ में विद्युत के प्रवाह में मदद करते हैं|
Q27. What is dynamo? On what principle does it work? Describe the structure and function of alternating current dynamo.
{डायनेमो क्या है? यह किस सिद्धांत पर कार्य करता है? प्रत्यावर्ती धारा डायनेमो की बनावट और कार्य का वर्णन करें|}
Ans. Dynamo (also called generator) is a device which convert mechanical energy into electricity.
Principle:- Electric generator work on the phenomenon of “electromagnetic induction”, when a rectangular coil is rotate in a magnetic field then an electric current is induced in the coil. Working:- When the axel connected to the two rings are rotated in such a way that the arm AB moves up and the arm CD moves down (let us say in clockwise) in the magnetic field, then the coil intersects the magnetic fields. Then induced currents are generated in these arms along the direction AB and CD i.e, in the direction of ABCD. This shows that the current in the external circuit flows from
Working:- When the axel connected to the two rings are rotated in such a way that the arm AB moves up and the arm CD moves down (let us say in clockwise) in the magnetic field, then the coil intersects the magnetic fields. Then induced currents are generated in these arms along the direction AB and CD i.e, in the direction of ABCD. This shows that the current in the external circuit flows from to
. After half a rotation, arm AB starts moving down and CD moving up. As a result, the directions of the induced currents in both the arms change, producing the net induced current in the direction DCBA. Thus, the current in the external circuit now flows from
to
. Hence after every half rotation the polarity of the current in the respective arms changes. Thus, generator produce AC current.
{डायनेमो (जिसे जनित्र भी कहा जाता है) एक ऐसा उपकरण है जो यांत्रिक ऊर्जा को बिजली में परिवर्तित करता है|
सिद्धांत:- विद्युत जनित्र “विद्युत चुम्बकीय प्रेरण” की घटना पर काम करता है, जब एक आयताकार कुंडली को चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में घुमाया जाता है तो कुंडली में एक विद्युत धारा प्रेरित होता है|  कार्यविधि:- जब दो वलयों से जुड़ी धुरी को इस तरह घुमाया जाता है कि कुंडली की भुजा AB ऊपर की ओर और भुजा CD नीचे की ओर (मान लीजिए दक्षिणावर्त में) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में गति करती है, तो कुंडली चुंबकीय क्षेत्रों को काटती है| तो इन भुजाओं में AB और CD दिशाओं के अनुदिश प्रेरित विद्युत धाराएँ प्रवाहित होने लगती हैं अर्थात ABCD की दिशा में| इसका तात्पर्य यह है कि बाह्य परिपथ में
कार्यविधि:- जब दो वलयों से जुड़ी धुरी को इस तरह घुमाया जाता है कि कुंडली की भुजा AB ऊपर की ओर और भुजा CD नीचे की ओर (मान लीजिए दक्षिणावर्त में) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में गति करती है, तो कुंडली चुंबकीय क्षेत्रों को काटती है| तो इन भुजाओं में AB और CD दिशाओं के अनुदिश प्रेरित विद्युत धाराएँ प्रवाहित होने लगती हैं अर्थात ABCD की दिशा में| इसका तात्पर्य यह है कि बाह्य परिपथ में से
की दिशा में विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है| अघूर्णन के बाद भुजा AB नीचे की ओर और CD ऊपर की ओर जाने लगती है| परिणामस्वरूप इन दोनों भुजाओं में प्रेरित विद्युत धारा की दिशा बदल जाती हैं और DCBA के अनुदिश नेट प्रेरित विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है| इस प्रकार, अब बाह्य परिपथ में
से
की दिशा में विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है| इसलिए प्रत्येक आधे घूर्णन के पश्चात क्रमित रूप से इन भुजाओं में विद्युत धारा की ध्रुवता बदलती रहती है| इस प्रकार, जनित्र AC धारा उत्पन्न करती है|
Q28. What are magnetic field lines? Write three properties of magnetic field lines. How can it be proved that magnetic field exists around a current carrying conductor?
{चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ क्या हैं? चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाओं के तीन गुणों को लिखिए| यह किस प्रकार प्रमाणित किया जा सकता है कि धारावाही चालक के चारों ओर चुंबकीय क्षेत्र होता है?}
Ans. (a) Magnetic field lines are imaginary lines around a magnet that represent the magnetic field of the magnet.
(b) Properties of magnetic field lines:-
(1) Magnetic field lines emerge from north pole and merge at the south pole.
(2) The direction of field lines inside the magnet is from its south pole to its north pole.
(3) No two field lines are found to cross one another.
(c) When a magnetic compass is placed closer to the current carrying conductor then it needle will get deflected, which proved that magnetic field exists around a current carrying conductor.
{(a) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ चुंबक के चारों ओर काल्पनिक रेखाएँ होती हैं जो चुंबक के चुंबकीय क्षेत्र को दर्शाती हैं|
(b) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाओं के गुण:-
(1) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ चुंबक के उत्तर ध्रुव से निकलती हैं और दक्षिणी ध्रुव पर विलीन हो जाती हैं|
(2) चुंबक के अंदर क्षेत्र रेखाओं की दिशा उसके दक्षिणी ध्रुव से उसके उत्तर ध्रुव की ओर होती है|
(3) दो क्षेत्र रेखाएँ कहीं भी एक दूसरे को प्रतिच्छेद (काटती) नहीं करती|
(c) जब एक चुंबकीय कंपास को विद्युत धारावाही चालक के करीब रखा जाता है तो उसकी सुई विक्षेपित हो जाती है, जो यह दर्शाता है कि धारावाही चालक के चारों ओर चुंबकीय क्षेत्र होता है|}
9113323460

I hope you like it. If you like then please share it and you can also Donate to our website by my number and QR code which is given above.
Thanks.
Next Chapter Sources of Energy (ऊर्जा के स्रोत)
Sources of Energy (ऊर्जा के स्रोत)
