Electricity (विद्युत)
Get “Electricity (विद्युत)” chapter’s previous years questions from 2009 to 2020 of JAC board.
Q1. Write S.I. unit of charge.
आवेश का S.I. मात्रक लिखिए|}
Ans. Coulomb
{कूलॉम}
Q2. Write the S.I. unit of potential difference.
{विभवान्तर का S.I. मात्रक लिखिए|}
Ans. Volt
{वोल्ट}
Q3. Write one source of direct current.
{दिष्टधारा के एक स्रोत का नाम लिखिए|}
Ans. Battery
{बैटरी}
Q4. Which instrumental is used to measure the electric current.
{विद्युत धारा को मापने के लिए किस यंत्र का प्रयोग किया जाता है?}
Ans. Ammeter
{ऐमीटर}
Q5. How is voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure potential difference between two points?
{किसी विद्युत परिपथ में दो बिंदुओं के बीच विभवांतर मापने के लिए वोल्टमीटर को किस प्रकार संयोजित किया जाता है?}
Ans. Parallel connection
{पार्श्वक्रम संयोजन}
Q6. Name one safety measure commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
{विद्युत परिपथों और साधित्रों में सामान्यतः उपयोग किए जाने वाले एक सुरक्षा उपाय का नाम बताइए|}
Ans. Electric fuse
{विद्युत फ्यूज}
Q7. Kilowatt-hour(kWh) is the unit of which quantity?
{किलोवाट-घंटा (kWh) किस राशि का मात्रक है?}
Ans. Electric energy
{विद्युत ऊर्जा}
Q8. How is ammeter connected in an electric circuit?
{किसी विद्युत परिपथ में ऐमीटर को किस क्रम में संयोजित किया जाता है?}
Ans. Series connection
{श्रेणीक्रम संयोजन}
Q9. What is the name of the device that measures the potential difference?
{विभवांतर मापने वाले यंत्र का नाम लिखिए|}
Ans. Voltmeter
{वोल्टमीटर}
Q10. Name the device which helps in maintain the potential difference across the ends of a conductor
{उस युक्ति का नाम लिखिए जो किसी चालक के सिरों पर विभवांतर को बनाए रखने में सहायता करती है}
Ans. Cell or Battery
{सेल या बैटरी}
Q11. Determine the rate at which energy is delivered by a current.
{विद्युत धारा द्वारा प्रदत्त ऊर्जा की दर का निर्धारण करें|}
Ans. The rate at which energy is delivered by a current is called power.
and
{विद्युत धारा द्वारा प्रदत्त ऊर्जा की दर को शक्ति कहलाती है| and
and }
Q12. Why is parallel arrangement of wires used in domestic wiring.
{घरेलू परिपथों में तारों की पार्श्व व्यवस्था का उपयोग क्यों किया जाता है?}
Ans. In parallel connection,
(1) total resistance will decrease.
(2) potential difference is same for all appliances .
(3) current are divided across the all appliances which is helpful to operate each appliances of having different resistance.
(4) we can operate each appliances separately.
{पार्श्वक्रम परिपथ में,
(1) कुल प्रतिरोध घट जाता है|
(2) सभी उपकरणों के लिए विभवान्तर समान होती है|
(3) विद्युत धारा सभी उपकरणों में विभाजित होती है जो अलग-अलग प्रतिरोध वाले प्रत्येक उपकरणों को संचालित करने में सहायक होते हैं|
(4) हम प्रत्येक उपकरण को अलग से संचालित कर सकते हैं|}
Q13. Give reason why metal conduct electricity.
{कारण बताएँ कि धातु विद्युत का संचालन क्यों करती है|}
Ans. Inside a metal, the free electrons generally move in all direction inside the atoms of the metal. Hence, there is no net flow of charge in any direction. But, when electricity is passing through the metal then free electrons move in one direction and an electric current start flowing through the metal. Hence, metal conduct electricity.
{एक धातु के अंदर, मुक्त इलेक्ट्रॉन आमतौर पर धातु के परमाणुओं के अंदर सभी दिशाओं में चलते रहते हैं| इसलिए, किसी भी दिशा में आवेश का शुद्ध प्रवाह नहीं होता है| लेकिन, जब बिजली धातु से गुजरती है तो मुक्त इलेक्ट्रॉन एक दिशा में चलने लगते हैं और धातु में विद्युत प्रवाह होने लगती है| इसलिए, धातु बिजली का संचालन करती है|}
Q14. Calculate the equivalent resistance of two resistance 4Ω and 16Ω, when they are connected in parallel.
{4Ω और 16Ω के प्रतिरोधों को समांतर क्रम में जोड़ने पर समतुल्य प्रतिरोध की गणना कीजिए|}
Ans. Ω,
Ω
Ω
Q15. There are 10 LED bulbs of 12W each and 5 fans of 75W each in a house. They are used for 10 hours per day. Prepare the bill for the month of February, 2020 if the rate is Rs.6 per unit.
{एक घर में 12W के 10 LED बल्ब और 75W के 5 पंखे लगे हैं| ये प्रतिदिन 10 घंटा उपयोग में लाये जाते हैं| फरवरी, 2020 का बिल तैयार कीजिए, यदि दर 6रु. प्रति यूनिट हो|}
Ans. Power consumed by 10 bulb
=10×12=120W
Power consumed by 5 fans
=5×75=375W
Total energy consumed in 1 day
=Total power consumed × time
=(120+375)×10=4950Wh
Energy consumed in Feb, 2020
=4950×29
=143550Wh
Cost
{10 बल्ब द्वारा उपयोग शक्ति
=10×12=120W
5 पंखों द्वारा उपयोग शक्ति
=5×75=375W
1 दिन में खपत की गई कुल ऊर्जा
= कुल उपयोग शक्ति × समय
=(120+375)×10=4950Wh
फरवरी, 2020 में खपत हुई ऊर्जा
=4950×29
=143550Wh
मूल्य
}
Q16. How can three resistors of resistance 3Ω, 6Ω and 9Ω are connected to give a total resistance of (a) 18Ω, (b) Ω?
{3Ω, 6Ω और 9Ω कुल प्रतिरोध के तीन प्रतिरोधकों को किस प्रकार संयोजित करेंगे कि संयोजत का कुल प्रतिरोध (a) 18Ω, (b) Ω हो?}
Ans. Ω,
Ω and
Ω
(a) In series connectionΩ
(b) In parallel connection
Ω
{Ω,
Ω और
Ω
(a) श्रेणीक्रम संयोजन में Ω
(b) पार्श्वक्रम संयोजन में
Ω }
Q17. (a) Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
(b) What is meant by the potential difference between two points beings 1V?
{(a) विद्युत टोस्टरों और विद्युत इस्तरियों के तापन अवयव शुद्ध धातु के बजाय किसी मिश्रधातु से क्यों बने होते हैं?
(b) दो बिंदुओं के बीच का विभवांतर 1V होने का क्या तात्पर्य है?}
Ans. (a) Resistivity of alloy is higher in comparison to its constituents metals. Alloys do not burn(oxidise) quickly at high temperature.
For ex:- The resistivity of alloy of Cu and Ni is greater than both resistivity of Cu and Ni.
So thats why the coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal.
(b) One volt is the potential difference between two points in a conductor carrying current, when 1 joule of work is done to move a charge of 1 coulomb from one point to the another.
i.e
{(a) मिश्रधातु की प्रतिरोधकता उनकी अवयवी धातुओं की तुलना में अधिक होती है| मिश्रधातुओं का उच्च ताप पर जल्दी ही उपचयन (दहन) नहीं होता|
उदाहरण के लिए:- Cu और Ni के मिश्रधातु की प्रतिरोधकता Cu और Ni दोनों की प्रतिरोधकता से अधिक होती है|
यही कारण है कि विद्युत टोस्टरों और विद्युत इस्तरियों के तापन अवयव शुद्ध धातु के बजाय किसी मिश्रधातु से बने होते हैं|
(b) यदि किसी विद्युत धारावाही चालक के दो बिंदुओं के मध्य एक कूलॉम आवेश को एक बिंदु से दूसरे बिंदु तक ले जाने में 1 जूल कार्य किया जाता है तो उन दो बिंदुओं के बीच विभवांतर 1 वोल्ट होता है|
यानी }
Q18. 4Ω, 8Ω, 12Ω and 24Ω, how will the four coils of the resistors be connected by that combination
(a) maximum
(b) lowest resistance can be achieved?
{4Ω, 8Ω, 12Ω और 24Ω, प्रतिरोधक की चार कुंडलियों को किस प्रकार संयोजित करेंगे की संयोजन से
(a) अधिकतम
(b) सबसे कम प्रतिरोध प्राप्त किया जा सके?}
Ans. (a) For maximum resistance
We shall connect this resistances in “series”.
i.e, Ω
(b) For lowest resistance
We shall connect this resistances in “parallel”.
i.e,
Ω
{(a) अधिकतम प्रतिरोध के लिए
हम प्रतिरोधकों को “श्रेणीक्रम” में जोड़ेंगे|
अर्थात, Ω
(b) सबसे कम प्रतिरोध के लिए
हम प्रतिरोधकों को “पार्श्वक्रम” में जोड़ेंगे|
अर्थात,
Ω}
Q19. What is series combination? Three resistances ,
and
are connected in series. Show that their equivalent resistance
.
{श्रेणीक्रम संयोजन किसे कहते है? तीन प्रतिरोध ,
एवं
श्रेणीक्रम संयोजित हैं| दर्शाइए कि उनका समतुल्य प्रतिरोध
है|}
Ans. (a) When two or more resistors are connected end to end continuously, then this combination is called series combination.
(b)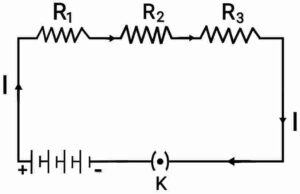 Let 3 resistors
Let 3 resistors ,
and
are connected in series,
,
and
are potential difference through the individual resistors
and be the current across the circuit.
So,
Now, applying Ohm’s law to whole circuit
On applying Ohm’s law to each resistors
Now, putting the equations (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) in equation(i)
Or
{(a) जब दो या दो से अधिक प्रतिरोधकों को लगातार एक सिरे से दूसरा सिरा मिलकर जोड़ा जाता हैं, तो यह श्रेणीक्रम संयोजन कहलाता है|
(b) माना की
माना की ,
और
3 प्रतिरोध श्रेणीक्रम में जुड़े हुए हैं,
,
और
अलग अलग प्रतिरोधकों का विभवांतर है
और परिपथ में विद्युत धारा है|
तो,
अब, ओम के नियम अनुसार पुरे परिपथ में
ओम के नियम अनुसार 3 अलग अलग प्रतिरोधकों में
अब, समीकरणों (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) को समीकरण (i) में रखने पर
Or }
Q20. State Ohm’s law and give its experimental verification.
{ओम का नियम लिखिए और इसका प्रायोगिक सत्यापन कीजिए|}
Ans. (a) The electric current flowing across a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V through its ends, provided its temperature remains the same. This is known as Ohm’s law.
i.e,
or
or
or
Where, V is the voltage across the metallic wire, is the current flowing through the wire and R is the resistance provided by the wire to the flow of current.
(b)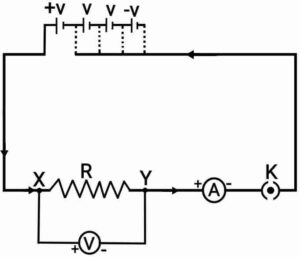 As in given figure,
As in given figure,
First of all use only one cell as the source of electricity in the circuit. Note the reading of the ammeter and the voltmeter.
Now connect two cells in the circuit and note the respective readings of the ammeter and voltmeter.
Repeat the above steps by using three cell again and then four cells in the circuit separately.
In this activity, approximately the identical value for is obtained in each case. When we make the graph of the current against the potential difference, it will be straight line. This shows that the current is proportional to the potential difference.
{(a) किसी धातु के तार में प्रवाहित होने वाली विद्युत धारा उस तार के सिरों के मध्य विभवांतर के अनुक्रमानुपाती होती हैं, लेकिन तार का ताप समान रखना चाहिए| इसे ओम का नियम कहते हैं|
अर्थात,
यानि,
अथवा
अथवा
जहाँ, V धातु के तार के सिरों के वोल्टेज है, तार से बहने वाली विद्युत धारा है और R तार द्वारा धारा के प्रवाह को प्रदान किया गया प्रतिरोध है|
(b) जैसा कि चित्र में दिया गया है,
जैसा कि चित्र में दिया गया है,
सबसे पहले परिपथ में विद्युत धारा के स्रोत के रूप में केवल एक सेल का प्रयोग कीजिये| ऐमीटर तथा वोल्टमीटर के पाठ्यांक नोट कीजिए|
अब परिपथ में दो सेलों को जोड़िए और ऐमीटर तथा वोल्टमीटर के पाठ्यांक नोट कीजिए|
उपरोक्त चरणों को पहले तीन सेल व फिर चार सेलों को परिपथ में अलग-अलग लगाकर दोहराएँ|
इस क्रियाकलाप में आप यह समझेंगे कि प्रत्येक प्रकरण में का लगभग एक ही मान प्राप्त होता है| जब हम विभवान्तर के विरुद्ध धारा का ग्राफ बनाते हैं, तो वह सीधी रेखा होगी| इससे पता चलता है कि धारा विभवान्तर के अनुक्रमानुपाती होता है|}
Q21. (a) On which factors does the resistance of a conductor depend?
(b) How can three resistors of resistances 2Ω , 3Ω and 6Ω be connected to give a total resistance of 11Ω and 1Ω.
{(a) किसी चालक का प्रतिरोध किन कारकों पर निर्भर करता है?
(b) प्रतिरोध 2Ω, 3Ω और 6Ω के तीन प्रतिरोधों को किस प्रकार संयोजित करें कि संयोजन का कुल प्रतिरोध 11Ω और 1Ω हो|}
Ans. (a) Resistance of a conductor depend:-
(i) on its area of cross section.
(ii) on its length.
(iii) on the nature of its material.
(b) Ω,
Ω and
Ω
(i) In series connectionΩ
(ii) In parallel connection
Ω
{(a) एक चालक का प्रतिरोध निर्भर करता है:-
(i) उसके अनुप्रस्थ काट के क्षेत्रफल पे|
(ii) चालक की लंबाई पे|
(iii) उसके पदार्थ की प्रकृति पे|
(b) Ω,
Ω और
Ω
(i) श्रेणीक्रम संयोजन में Ω
(ii) पार्श्वक्रम संयोजन में
Ω }
Q22. How can three resistors of resistances 2Ω , 3Ω and 6Ω be connected to give a total resistance of
(a) 11Ω
(b) 1Ω
(c) 4Ω
{2Ω , 3Ω और 6Ω प्रतिरोध के तीन प्रतिरोधों को किस प्रकार संयोजित करेंगे की संयोजन का कुल प्रतिरोध
(a) 11Ω
(b) 1Ω
(c) 4Ω हो?}
Ans. Ω,
Ω and
Ω
(a) In series connectionΩ
(b) In parallel connection
Ω
(c) Connect in series with the parallel combination
and
Ω
{Ω,
Ω और
Ω
(a) श्रेणीक्रम संयोजन में Ω
(b) पार्श्वक्रम संयोजन में
Ω
(c) को श्रेणीक्रम में पार्श्वक्रम संयोजन
और
के साथ जोड़ेंगे|
Ω }
Q23. (a) Why is series connection not used in domestic electrical circuits?
(b) Calculate the following on the basis of the circuit shown in the following figure: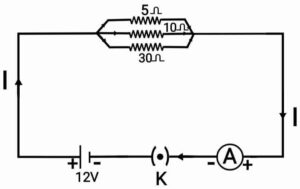 (i) The value of the current flowing through each resistor.
(i) The value of the current flowing through each resistor.
(ii) The value of the total current affected in the circuit.
(iii) The total effective resistance of the circuit.
{(a) घरेलू विद्युत परिपथों में श्रेणीक्रम संयोजन का उपयोग क्यों नहीं किया जाता है?
(b) निम्न चित्र में दिखाए गए परिपथ के आधार पर निम्नलिखित को परिकलित कीजिए: (i) प्रत्येक प्रतिरोधक से प्रवाहित होने वाली धारा का मान|
(i) प्रत्येक प्रतिरोधक से प्रवाहित होने वाली धारा का मान|
(ii) परिपथ में प्रभावित कुल धारा का मान|
(iii) परिपथ का कुल प्रभावी प्रतिरोध|}
Ans. (a) It is impracticable to join all components (such as heater, bulb etc) in series because they required current of different values. If one component fails then circuit become disconnected and none of the components works.
(b) (i) Current in resistor
Current in resistor
Current in resistor
(ii) For total current
(iii) For total resistance
Ω
{(a) श्रेणीक्रम में सभी साधित्रों (जैसे हीटर, बल्ब इत्यादि) को जोड़ना असंभव है क्योंकि उन्हें विभिन्न मूल्यों के विद्युत धारा की आवश्यकता होती है| जब एक अवयव कार्य करना बंद कर देता है तो परिपथ टूट जाता है और परिपथ का दूसरा कोई अवयव काम नहीं करता है|
(b) (i) प्रतिरोधक में धारा
प्रतिरोधक में धारा
प्रतिरोधक में धारा
(ii) कुल धारा के लिए
(iii) प्रतिरोध के लिए
Ω }
Q24. (a) If the resistance of the filament of an electric bulb is 1200Ω, then how much current will that bulb draw from a 220V source?
(b) How to connect four coils of resistance 4Ω, 8Ω, 12Ω and 24Ω so that the combination can get (i) 48Ω (ii) 2Ω
{(a) यदि किसी विद्युत बल्ब के तंतु का प्रतिरोध 1200Ω है, तो वह बल्ब 220V स्रोत से कितनी धारा खींचेगा?
(b) 4Ω, 8Ω, 12Ω और 24Ω प्रतिरोध की चार कुंडलियों को कैसे जोड़ा जाए ताकि संयोजन से (i) 48Ω (ii) 2Ω प्रतिरोध प्राप्त हो सके?}
Ans. (a) Potential difference=220V,
Resistance=1200Ω
Now,
(b) Ω,
Ω,
Ω,
Ω
(i) In series connectionΩ
(ii) In parallel connection
Ω
{(a) विभवांतर=220V, प्रतिरोध=1200Ω
अब,
(b) Ω,
Ω,
Ω,
Ω
(i) श्रेणीक्रम संयोजन में Ω
(ii) पार्श्वक्रम संयोजन में
Ω}
Q25. (i)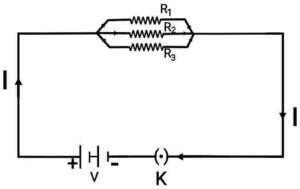 In the circuit diagram of the given figure, suppose the values of resistors
In the circuit diagram of the given figure, suppose the values of resistors ,
and
are 5Ω, 10Ω and 30Ω respectively and they are connected to a 12V battery. Calculate
(a) the current through each resistor
(b) the total current through the circuit
(c) the total resistance of the circuit.
(ii) An electric bulb is connected to a 220V generator. If 0.50A current flows through the bulb, what is the power of the bulb.
(iii) Define the unit of electric current.
{(i) दी गई आकृति के परिपथ आरेख में, मान लीजिए कि प्रतिरोधकों
दी गई आकृति के परिपथ आरेख में, मान लीजिए कि प्रतिरोधकों ,
और
के मान क्रमशः 5Ω, 10Ω और 30Ω है और वे 12V की बैटरी से संयोजित किया गया हैं| गणना करे:-
(a) प्रत्येक प्रतिरोधक से प्रवाहित विद्युत धारा
(b) परिपथ में प्रवाहित कुल विद्युत धारा
(c) परिपथ का कुल प्रतिरोध|
(ii) एक बिजली के बल्ब 220V के जनरेटर से संयोजित है| यदि बल्ब से 0.50A विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है, तो बल्ब की शक्ति क्या है?
(iii) विद्युत धारा के मात्रक की परिभाषा लिखिए|}
Ans. (i) (a) Current in resistor
Current in resistor
Current in resistor
(b) For total current
(c) For total resistance
Ω
(ii) Power=Energy current
(iii) The S.I unit of current is called “ampere” (A).
One ampere is formed by the flow of 1 coulomb of charge in per second through the conductor.
{(i) (a) प्रतिरोधक में धारा
प्रतिरोधक में धारा
प्रतिरोधक में धारा
(b) कुल धारा के लिए
(c) प्रतिरोध के लिए
Ω
(ii) शक्ति=ऊर्जा धारा
(iii) विद्युत धारा के मात्रक को “ऐम्पियर” (A) कहा जाता है|
1 ऐम्पियर विद्युत धारा की रचना चालक से प्रति सेकेंड एक कूलॉम आवेश के प्रवाह से होती है|
}
Q26. A switch board has three switches out of which each one is meant for bulb, tube light and fans respectively. Switches are so connected that they can be used separately or all at once time. In which type are these switches connected to each other? Find an expression of equivalent resistance of this type of connection.
{एक स्विच बोर्ड में तीन स्विच लगे हैं जिनमें से प्रत्येक क्रमशः बल्ब, ट्यूब लाइट और पंखे के लिए है| सभी स्विचों को इस प्रकार जोड़ा गया है कि उन्हें अलग-अलग और एक साथ भी उपयोग किया जा सकता है| स्विच बोर्ड में स्विचों को एक दूसरे से किस क्रम में संयोजित किया गया है? इस प्रकार के संयोजन के लिए समतुल्य प्रतिरोध का व्यंजक ज्ञात कीजिए|}
Ans. These switches are connected in “parallel” to each other.
 Let
Let and
are the resistance of bulb, tube light and fan respectively are connected in parallel.
V is the potential difference of the source
and
are the current across the individual resistors
So,
Now, applying Ohm’s law to parallel combination
On applying Ohm’s law to each resistors
Now, putting the equation (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) in equation(i)
or
{ये स्विचें एक दूसरे से “पार्श्वक्रम” में जुड़े हुए हैं|
 माना की
माना की ,
और
क्रमशः बल्ब, ट्यूबलाइट और पंखे के प्रतिरोध पार्श्वक्रम में जुड़े हुए हैं,
V स्रोत का विभवांतर है
और और
अलग-अलग प्रतिरोधों में विद्युत धारा हैं|
तो,
अब, पार्श्वक्रम संयोजन पर ओम का नियम लागू करने पर
प्रत्येक प्रतिरोधक पर ओम का नियम लागू करने पर
अब, समीकरणों (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) को समीकरण (i) में रखने पर
or }
Q27. (i) State Ohm’s law
(ii) Calculate the following on the basis of the circuit shown in the following figure: (a) The value of the current flowing through each resistor.
(a) The value of the current flowing through each resistor.
(b) The value of the total current affected in the circuit.
(c) The total effective resistance of the circuit.
(iii) Convert 1kwh to joule
{(i) ओम का नियम लिखिए
(ii) निम्न चित्र में दिखाए गए परिपथ के आधार पर निम्नलिखित को परिकलित कीजिए: (a) प्रत्येक प्रतिरोधक से प्रवाहित होने वाली धारा का मान|
(a) प्रत्येक प्रतिरोधक से प्रवाहित होने वाली धारा का मान|
(b) परिपथ में प्रभावित कुल धारा का मान|
(c) परिपथ का कुल प्रभावी प्रतिरोध|
(iii) 1kWh को जूल में बदलें}
Ans. (i) The electric current flowing across a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V through its ends, provided its temperature remains the same. This is known as Ohm’s law.
i.e,
or
or
or
Where, V is the voltage across the metallic wire, is the current flowing through the wire and R is the resistance provided by the wire to the flow of current.
(ii) (a) Current in resistor
Current in resistor
Current in resistor
(b) For total current
(c) For total resistance
Ω
(iii) 1 kwh=1000 watt × 3600 sec 1 kwh=3.6 ×
watt sec
1 kwh=3.6 ×
joule
{(i) किसी धातु के तार में प्रवाहित होने वाली विद्युत धारा उस तार के सिरों के मध्य विभवांतर के अनुक्रमानुपाती होती हैं, लेकिन तार का ताप समान रखना चाहिए| इसे ओम का नियम कहते हैं|
अर्थात,
अथवा
अथवा
अथवा
जहाँ, V धातु के तार के सिरों के वोल्टेज है, तार से बहने वाली विद्युत धारा है और R तार द्वारा धारा के प्रवाह को प्रदान किया गया प्रतिरोध है|
(ii) (a) प्रतिरोधक में धारा
प्रतिरोधक में धारा
प्रतिरोधक में धारा
(b) कुल धारा के लिए
(c) प्रतिरोध के लिए
Ω
(iii) 1 kwh=1000 वाट × 3600 सेकंड 1 kwh=3.6 ×
वाट सेकंड
1 kwh=3.6 ×
जूल}
9113323460

I hope you like it. If you like then please share it and you can also Donate to our website by my number and QR code which is given above.
Thanks.
Next Chapter Magnetic Effects of Electric Current (विद्युत धारा के चुंबकीय प्रभाव)
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current (विद्युत धारा के चुंबकीय प्रभाव)
