Control and Coordination (नियंत्रण और समन्वय)
Get “Control and Coordination” chapter’s previous years questions from 2009 to 2020 of JAC board.
Q1. Name the hormone that catalyzes fall of leaves.
{उस पादप हार्मोन का नाम बताइए जो पतझड़ को उत्प्रेरित करता है|}
Ans. Abscisic acid
{एब्सिसिक अम्ल}
Q2. Give an example of a plant hormone that stimulates growth.
{उस पादप हार्मोन का उदाहरण दीजिए जो वृद्धि को बढ़ाता है|}
Ans. Auxin
{ऑक्सिन}
Q3. Name a plant hormone which is a component of plant growth.
{एक पादप हॉर्मोन का नाम लिखिए जो पादप वृद्धि का एक घटक है|}
Ans. Auxin
{ऑक्सिन}
Q4. What is the principal co-ordinating centre of body?
{शरीर का प्रमुख समन्वय केंद्र क्या है?}
Ans. Brain
{मस्तिष्क}
Q5. The excess of which hormone causes excessive increase of calcium in blood?
{किस हार्मोन की अधिकतम से रक्त में कैल्शियम की मात्रा अधिक बढ़ जाती है?}
{हमारे शरीर में ग्राही का क्या कार्य है? ग्राही के कार्य न करने पर क्या समस्याएँ उत्पन्न हो सकती हैं?}
Ans. Parathyroid glands
{परावटु ग्रंथि}
Q6. Write the name of the factor which develops an impulse.
{आवेग उत्पन्न करने वाले कारक का नाम लिखिए|}
Ans. Neurons
{न्यूरॉन्स}
Q7. What is the target organ of adrenaline hormone?
{एड्रिनेलिन हार्मोन किस अंग पर सीधा कार्य करता है?}
Ans. Heart
{हृदय}
Q8. Which element is essential in the secretion of thyroxine?
{थायरॉक्सिन के स्रावण में कौन तत्व आवश्यक है?}
Ans. Iodine
{आयोडीन}
Q9. How does an excess of insulin hormone affect the glucose level of the blood??
{इन्सुलिन हार्मोन की अधिकता से रुधिर के ग्लूकोज स्तर पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ता है?}
Ans. Excess of insulin hormones fall the sugar level in the blood.
{इन्सुलिन हार्मोन की अधिकता से रक्त में शर्करा के स्तर गिर जाता है|}
Q10. Which hormone controls the level of sugar in the blood?
{कौन सा हार्मोन रुधिर में शर्करा के स्तर को नियंत्रित करता है?}
Ans. Insulin
{इन्सुलिन}
Q11. Why do some multicellular organisms apply chemical communication instead of nervous communication?
{कुछ बहुकोशिकीय जीव तंत्रिकीय संचार के बजाय रासायनिक संचार का उपयोग क्यों करते हैं?}
Ans. Chemical communication is done by hormones and it does not require any special tissue like nervous tissue for signaling to take place.
But nervous communication is done by nervous tissue and those cell are not able to communicate which is not connected to nervous tissues.
{रासायनिक संचार हार्मोन द्वारा किया जाता है और इसे संकेत करने के लिए तंत्रिका ऊतक जैसे किसी विशेष ऊतक की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है|
लेकिन तंत्रिकीय संचार तंत्रिका ऊतक द्वारा किया जाता है और वे कोशिकाएँ संचार करने में सक्षम नहीं होती हैं जो तंत्रिका ऊतकों से जुड़ी नहीं होती हैं|}
Q12. What do you mean by sensory and motor neurons.
{संवेदी और प्रेरक तंत्रिकाओं से आप क्या समझते हैं?}
Ans. Sensory neurons carry signals from the outer part of the body into the brain or spinal cord.
Motor neurons carry signals from the brain or spinal cord to the outer parts of the body.
{संवेदी तंत्रिका शरीर के बाहरी हिस्से से मस्तिष्क या मेरुरज्जु में संकेत ले जाते हैं|
प्रेरक तंत्रिका मस्तिष्क या मेरुरज्जु से संकेतों को शरीर के बाहरी हिस्सों तक ले जाते हैं|}
Q13. What is diabetes? Why does this happen?
{मधुमेह क्या है? यह क्यों होता हैं|}
Ans. Diabetes is a disease that occurs when sugar level in our body rise. If insulin hormone (which is secreted by the pancreas) is not released in proper amount, then sugar level in the body rises and it results diabetes occurs.
{मधुमेह एक ऐसी बीमारी है जो तब होती है जब हमारे शरीर में शर्करा का स्तर बढ़ जाता है| यदि इंसुलिन हार्मोन (जो अग्न्याशय द्वारा स्रावित होता है) उचित मात्रा में नहीं निकलता है, तो शरीर में शर्करा का स्तर बढ़ जाता है और इसके परिणामस्वरूप मधुमेह होता है|}
Q14. Write the names of A, B, C and D as directed in the figure.
{चित्र में निर्देशित A, B, C और D के नाम लिखें}
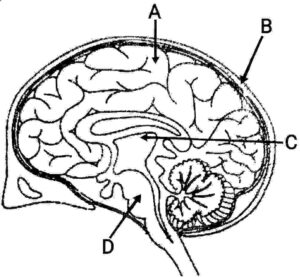
Ans. A- Cerebrum
B- Cranium (Skull)
C- Mid-brain
D- Pons (Part of hind-brain)
{A- प्रमस्तिष्क
B- कपाल (खोपड़ी)
C- मध्यमस्तिष्क
D- पॉन्स (पश्चमस्तिष्क का हिस्सा) }
Q15. Define reflex action and write any one example.
{प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया को परिभाषित कीजिए तथा कोई एक उदाहरण लिखिए|}
Ans. The sudden and rapid reaction of the body parts which is controlled by the spinal cord is called reflex action.
It is an involuntary action.
For ex:- Rapid moving of our hand when we touch a flame.
शरीर के अंगों की अचानक और तीव्र प्रतिक्रिया जो मेरुरज्जु द्वारा नियंत्रित होता है, प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया कहलाती है|
यह एक अनैच्छिक क्रिया है|
उदाहरण:- जब हम किसी ज्वाला को छूते हैं तो हमारा हाथ तेजी से हट जाता है|}
Q16. Difference between phototropism and gravitropism.
{प्रकाशनुवर्त्तन और गुरुत्वानुवर्त्तन में क्या अंतर है?}
Ans.
| Phototropism | Gravitropism |
| (1) The direction of the movement of plants is either towards the light or away from the light. | (1) The direction of the movement of plants is either towards the earth/gravity or away from it. |
| (2) Ex:- Shoots respond by bending towards light while roots respond by bending away from it. | (2) Ex:- Root respond by pulling towards earth or gravity while shoots respond by away from it. |
{
| प्रकाशनुवर्त्तन | गुरुत्वानुवर्त्तन |
| (1) पौधों की गति की दिशा या तो प्रकाश की ओर या तो प्रकाश से विपरीत होती है| | (1) पौधों की गति की दिशा या तो पृथ्वी/गुरुत्व की ओर या तो उससे विपरीत होती है| |
| (2) उदाहरण:- प्ररोह प्रकाश की ओर झुककर अनुक्रिया करती हैं जबकि जड़ें उससे दूर मुड़कर अनुक्रिया करती हैं| | (2) उदाहरण: – जड़े पृथ्वी या गुरुत्व की ओर खींचकर अनुक्रिया करती है जबकि प्ररोह उससे विपरीत अनुक्रिया करती हैं| |
}
Q17. What is the cause of dwarfism in human?
{मनुष्य में बौनेपन का क्या कारण है?}
Ans. Growth hormones is one of the hormones released by the pituitary gland. It controlls growth and development of the body. If there is a deficiency of this hormone in childhood, it cause dwarfism.
{पीयूष ग्रंथि से स्रावित होने वाले हार्मोन में एक वृद्धि हार्मोन होते है| यह शरीर की वृद्धि और विकास को नियंत्रित करता है| यदि बाल्यकाल में इस हार्मोन की कमी हो जाती है, तो यह बौनापन का कारण बनता है|}
Q18. What are the adaptations of leaves of photosynthesis?
{प्रकाश संश्लेषण के लिए पत्तियों में कौन-से अनुकूलन होते हैं?}
Ans. (i) Leaf provide large surface area for the maximum light absorption.
(ii) Presence of numerous stomata on leaf’s surface for gaseous exchange and transpiration.
(iii) The extensive network of veins enable quick transport of food and water.
{{i) पत्ती अधिकतम प्रकाश अवशोषण के लिए बड़ा सतह क्षेत्र प्रदान करती है|
(ii) गैसीय विनिमय और वाष्पोत्सर्जन के लिए पत्ती की सतह पर अनेक रंध्रों की उपस्थिति|
(iii) नसों का व्यापक नेटवर्क भोजन और पानी के त्वरित परिवहन को सक्षम बनाता है|}
Q19. What is the difference between walking and reflex action?
{टहलने और प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया में क्या अंतर है?}
Ans.
| Reflex action | Walking |
| (1) This is an involuntary action. | (1) This is a voluntary action. |
| (2) It is a sudden and rapid reaction of the body parts. | (2) It is timely but slow response. |
| (3) It is controlled by the spinal cord . | (3) It is controlled by the brain. |
{
| प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया | टहलने |
| (1) यह एक अनैच्छिक क्रिया है| | (1) यह एक ऐच्छिक क्रिया है| |
| (2) यह शरीर के अंगों की अचानक और तीव्र प्रतिक्रिया है| | (2) यह समय पर लेकिन धीमी प्रतिक्रिया है| |
| (3) यह मेरुरज्जु द्वारा नियंत्रित होता है| | (3) यह मस्तिष्क द्वारा नियंत्रित होता है| |
}
Q20. What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
{प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया में मस्तिष्क की क्या भूमिका है?}
Ans. Brain has no direct role in the reflex action. Reflex action is a fast action and brain take some time to taking action. By which we can not do fast action in danger situation. So reflex action is mainly controlled by “spinal cord” as these actions do not required thinking and are very quick. Although the input information also goes on to reach the brain.
{प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया में मस्तिष्क की कोई प्रत्यक्ष भूमिका नहीं होती है| प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया एक तीव्र क्रिया है और मस्तिष्क को क्रिया करने में कुछ समय लगता है| जिससे हम खतरे की स्थिति में तेजी से क्रिया नहीं कर पाते हैं| इसलिए प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया मुख्य रूप से “मेरुरज्जु” द्वारा नियंत्रित होती है क्योंकि इन क्रियाओं में सोचने की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है और ये बहुत तेज़ होती हैं| हालांकि आगत सूचनाएँ दिमाग तक भी जाती रहती है|}
Q21. Write three differences between reflex action and reflex arc.
{प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया और प्रतिवर्ती चाप में तीन अंतर लिखिए|}
Ans.
| Reflex action | Reflex Arc |
| (1) The sudden and rapid reaction of the body parts is called reflex action. | (1) The reflex arc is the nerve pathway that is followed by reflex action. |
| (2) It is controlled by the spinal cord . | (2) This pathway is present between in the nerve cell and spinal cord. |
| (3) This is an involuntary action. | (3) Hear, signal is detected by neurons and transport it into spinal cord, where motor neurons received this signal and then reflex action is take place by the body part. |
{
| प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया | प्रतिवर्ती चाप |
|
(1) शरीर के अंगों की अचानक और तीव्र प्रतिक्रिया को प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया कहा जाता है| |
(1) प्रतिवर्ती चाप तंत्रिका मार्ग है जो प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया द्वारा अनुसरण किया जाता है| |
|
(2) यह मेरुरज्जु द्वारा नियंत्रित होता है| |
(2) यह भाग तंत्रिका कोशिका और मेरुरज्जु के बीच मौजूद होता है| |
| (3) यह एक अनैच्छिक क्रिया है| | (3) यहाँ, तंत्रिका कोशिका द्वारा संकेत पता लगाया जाता है और इसे मेरुरज्जु में ले जाता है, जहाँ प्रेरक तंत्रिका कोशिका इस संकेत को प्राप्त करते है और फिर शरीर के अंग द्वारा प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया की जाती है|} |
}
Q22. What is the function of receptor in our body? What problems can originate when receptors do not work?
{हमारे शरीर में ग्राही का क्या कार्य है? ग्राही के कार्य न करने पर क्या समस्याएँ उत्पन्न हो सकती हैं?}
Ans. Receptors are the special type of nerve cell which is also called neuron. These receptors are present in our all body parts such as ear, tongue, nose etc. Dendritic tip of neuron detect all information from our environment such as taste, smell, touch etc and give this signal to the spinal cord and brain.
If receptor do not work properly, then receptor could not be able to detect any information from the environment and send to the brain. This occurs lot of damage such as we can not able to taste, smell, stimulus on heat or fire etc.
{ग्राही एक विशेष प्रकार की तंत्रिका कोशिका होती है जिसे न्यूरॉन भी कहा जाता है| ये ग्राही हमारे शरीर के सभी अंगों जैसे कान, जीभ, नाक आदि में मौजूद होते हैं| न्यूरॉन की द्रुमाकृतिक सिरे हमारे पर्यावरण से स्वाद, गंध, स्पर्श आदि जैसी सभी सूचनाओं का पता लगाती है और मेरुरज्जु और मस्तिष्क को यह संकेत देती है|
यदि ग्राही ठीक से काम नहीं करता है, तो ग्राही पर्यावरण से किसी भी जानकारी का पता लगाने और मस्तिष्क को भेजने में सक्षम नहीं हो सकता है| इससे बहुत नुकसान होता है जैसे कि हम स्वाद, गंध, गर्मी या आग पर उत्तेजना आदि में सक्षम नहीं होते हैं|
Q23. Write two differences between plant hormones and animal hormones.
{पादप हार्मोन और जंतु हार्मोन में दो अंतर लिखिए|}
Ans.
| Plant hormones | Animal hormones |
| (1) No specific organs are involved in the synthesis of the plant hormones. | (1) Animal hormones are synthesized in the endocrine gland. |
| (2) Plant hormones are transported through xylem, phloem or by diffusion. | (2) Animal hormones are transported by the blood. |
{
| पादप हार्मोन | जंतु हार्मोन |
| (1) पादप हार्मोन के संश्लेषण में कोई विशिष्ट अंग शामिल नहीं होता है| | (1) जंतु हार्मोन अंतः स्रावी ग्रंथि में संश्लेषित किये जाते हैं| |
| (2) पादप हार्मोन को जाइलेम, फ्लोएम या विसरण द्वारा पुरे पादप में पहुँचाया जाता है| | (2) जंतु हार्मोन को रक्त द्वारा पुरे शरीर में पहुँचाया जाता है| |
}
9113323460

I hope you like it. If you like then please share it and you can also Donate to our website by my number and QR code which is given above.
Thanks.
Next Chapter How do Organisms Reproduce (जीव जनन कैसे करते हैं)
How do Organisms Reproduce (जीव जनन कैसे करते हैं)
