Life Processes (जैव प्रक्रम)
Get “Life Processes” chapter’s previous years questions from 2009 to 2020 of JAC board.
Q1. What are the processes that are important for life?
{जीवन के लिए कौन सी प्रक्रम महत्वपूर्ण हैं?}
Ans. Nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion.
{पोषण, श्वसन, वहन, उत्सर्जन|}
Q2. Name the enzyme found in saliva.
{लार में पाए जाने वाले इनजाइम का नाम बताइए|}
Ans. Salivary amylase
{लार एमिलेस}
Q3. Which element is essential for the synthesis of compounds of protein?
{प्रोटीन के यौगिकों के संश्लेषण के लिए कौन सा तत्व आवश्यक है?}
Ans. Nitrogen
{नाइट्रोजन}
Q4. What should be the consequences of the deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
{हमारे शरीर में हीमोग्लोबिन की कमी के क्या परिणाम हो सकते हैं?}
Ans. When haemoglobin level will decrease in our body then blood could not be able to transport proper amount of oxygen to all our body cells due to which it cause deficiency of oxygen in our body or body’s cells and result as improper digestion.
{जब हमारे शरीर में हीमोग्लोबिन का स्तर कम हो जाता है तो रक्त हमारे शरीर की सभी कोशिकाओं तक उचित मात्रा में ऑक्सीजन नहीं पहुँचा पाता है जिसके कारण हमारे शरीर या शरीर की कोशिकाओं में ऑक्सीजन की कमी होती है और परिणामस्वरूप अनुचित पाचन होता है|}
Q5. Under what conditions the presence of a proper transport system in plants become essential?
{किन परिस्थितियों में पौधों में समुचित परिवहन तंत्र की उपस्थिति आवश्यक हो जाती है?}
Ans. If the distances between chlorophyll containing organs and soil containing organs are become large because of changs in plant design. Hence, diffusion process will not be sufficient to give raw material in the leaves and energy in roots. So that condition the presence of a proper transport system in plants become essential, i.e xylem and phloem.
{यदि पादप शरीर की अभिकल्पना में परिवर्तन के कारण मृदा के सम्पर्क वाले अंगों में और क्लोरोफिलयुक्त अंगों में दूरियाँ बढ़ जाती है तो पत्तियों में कच्ची सामग्री और जड़ों में ऊर्जा उपलब्ध कराने के लिए विसरण प्रक्रम काफी नहीं हैं| इस परिस्थितिओ में पौधों में समुचित परिवहन तंत्र की उपस्थिति आवश्यक हो जाती हैं, यानी जाइलम और फ्लोएम|}
Q6. How are alveoli designed for maximum exchange of gases.
{गैसों के अधिकतम विनिमय के लिए कुपिकाएँ किस प्रकार अभिकल्पित हैं?}
Ans. The wall of the alveoli have an extensive network of blood-vessels. Air is absorbed into lungs and fills the expanded alveoli. The blood vessels of alveoli exchange the oxygen and .
{कूपिकाओ की भित्ति में रुधिर वाहिकाओं का विस्तीर्ण जाल होता है| वायु फूफ्फस के अंदर चूस ली जाती है और विस्तृत कूपिकाओ को भर लेती है| कूपिकाओ का रुधिर वाहिकाओं ऑक्सीजन और का आदान-प्रदान करती हैं|
Q7. What is dialysis?
{अपोहन क्या है?}
Ans. When our kidney stop working or does not work properly then we use an artificial kidney in this case. Dialysis is a processes in which an artificial kidney is used to remove nitrogenous waste products from the blood.
जब हमारी वृक्क काम करना बंद कर देती है या ठीक से काम नहीं करती है तो ऐसे में हम एक कृत्रिम वृक्क का इस्तेमाल करते हैं| अपोहन एक ऐसी प्रक्रिया है जिसमें रक्त से नाइट्रोजनयुक्त अपशिष्ट उत्पादों को निकालने के लिए एक कृत्रिम वृक्क का उपयोग किया जाता है|}
Q8. What is blood? Write its any two functions.
{रक्त क्या है? इसके कोई दो कार्य लिखिए|}
Ans. Blood is a fluid connective tissue. Blood have of a fluid medium called Plasma in which the cells are suspended.
Functions:-
(1) Plasma transports food and carbon dioxide in dissolved form.
(2) Oxygen is transported by the red blood cells.
{रक्त एक तरल संयोजी ऊतक है| रक्त में एक तरल माध्यम (आधात्री) होता है जिसे प्लैज्मा कहा जाता है जिसमें कोशिकाएँ तैरती रहती हैं|
कार्य:-
(1) प्लैज्मा भोजन और कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड को विलीन रूप में वहन करता है|
(2) ऑक्सीजन को लाल रक्त कोशिकाएँ ले जाती हैं|}
Q9. Describe different stages of nutrition in amoeba.
{अमीबा में पोषण की विभिन्न अवस्थाओं का वर्णन कीजिए|}
Ans. Amoeba get food by using temporary finger-like extensions of the cell surface which fuse over the food particle making a food vacuole. Inside the food vacuole, complex substances are split up into the simplex ones which get diffuse into the cytoplasm. The remaining undigested material is transferred to the surface of the cell and thrown out.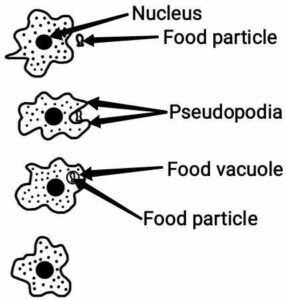
{अमीबा कोशिकीय सतह से अंगुली जैसे अस्थायी प्रवर्ध कूटपाद की मदद से भोजन ग्रहण करते है| यह प्रवर्ध भोजन के कणों को घेर लेता हैं व संगठित होकर खाद्य रिक्तिका बनाते हैं| खाद्य रिक्तिका के अंदर जटिल पदार्थों का विघटन सरल पदार्थों में किया जाता है तथा वे कोशिकाद्रव्य में विसरित हो जाते हैं| शेष अपचित पदार्थ कोशिका की सतह की ओर गति करता है और शरीर से बाहर निकाल दिया जाता है|
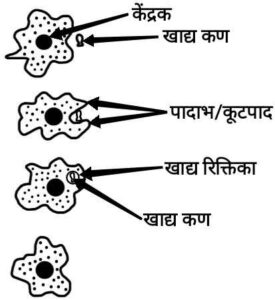 }
}
Q10. (a) What is blood? Write its two functions.
(b) Describe nutrition in amoeba.
{(a) रक्त क्या है? इसके दो कार्य लिखिए|
(b) अमीबा में पोषण का वर्णन कीजिए|}
Ans. (a) Blood is a fluid connective tissue. Blood have of a fluid medium called Plasma in which the cells are suspended.
Functions:-
(1) Plasma transports food and carbon dioxide in dissolved form.
(2) Oxygen is transported by the red blood cells.
(b) Amoeba get food by using temporary finger-like extensions of the cell surface which fuse over the food particle making a food vacuole. Inside the food vacuole, complex substances are split up into the similar ones which get diffuse into the cytoplasm. The remaining undigested material is transferred to the surface of the cell and thrown out.
{(a) रक्त एक तरल संयोजी ऊतक है| रक्त में एक तरल माध्यम (आधात्री) होता है जिसे प्लैज्मा कहा जाता है जिसमें कोशिकाएँ तैरती रहती हैं|
कार्य:-
(1) प्लैज्मा भोजन और कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड को विलीन रूप में वहन करता है|
(2) ऑक्सीजन को लाल रक्त कोशिकाएँ ले जाती हैं|
(b) अमीबा कोशिकीय सतह से अंगुली जैसे अस्थायी प्रवर्ध कूटपाद की मदद से भोजन ग्रहण करते है| यह प्रवर्ध भोजन के कणों को घेर लेता हैं व संगठित होकर खाद्य रिक्तिका बनाते हैं| खाद्य रिक्तिका के अंदर जटिल पदार्थों का विघटन सरल पदार्थों में किया जाता है तथा वे कोशिकाद्रव्य में विसरित हो जाते हैं| शेष अपचित पदार्थ कोशिका की सतह की ओर गति करता है और शरीर से बाहर निकाल दिया जाता है|
 }
}
Q11. Draw the labelled diagram of nephron.
(Description is not required.)
वृक्काणु या नेफ्रॉन का नामांकित चित्र बनाइए|
(वर्णन की आवश्यकता नहीं है|)
Ans. 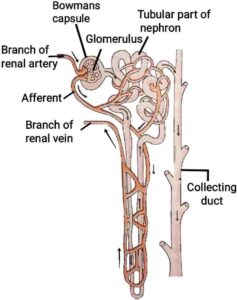
{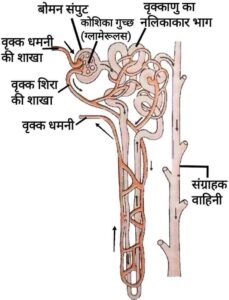
}
Q12. Describe the process of urine formation in kidneys with a diagram.
{गुर्दों में मूत्र निर्माण के प्रक्रम का सचित्र वर्णन कीजिए|}
Ans. Urine produced by the filter out waste products from the blood. Nitrogenous waste such as uric acid or urea are separated from blood in the kidneys. Each kidney has large number of filtration units known as nephrons (as shown in above figure). In the initial filtrate some substances, such as glucose, salt, amino acid and a major amount of water are remains present. As urine enters this tube, selective reabsorption of these substances takes place. This how formation of urine in kidney.
Urine produced by the filter out waste products from the blood. Nitrogenous waste such as uric acid or urea are separated from blood in the kidneys. Each kidney has large number of filtration units known as nephrons (as shown in above figure). In the initial filtrate some substances, such as glucose, salt, amino acid and a major amount of water are remains present. As urine enters this tube, selective reabsorption of these substances takes place. This how formation of urine in kidney.
{ मूत्र का उत्पादन, रुधिर में से अपशिष्ट पदार्थो को छानकर बाहर निकालने से बनता है| नाइट्रोजनी वर्ज्य पदार्थ जैसे यूरिया अथवा यूरिक अम्ल वृक्क में रुधिर से अलग कर लिए जाते हैं| प्रत्येक वृक्क में बहुत से निस्पंदन एकक होते हैं जिन्हें विक्काणु कहते है (जो कि ऊपर चित्र में है)| प्रारंभिक निस्यंद में कुछ पदार्थ, जैसे ग्लूकोज, लवण, अमीनो अम्ल और प्रचुर मात्रा में जल रह जाते है| जैसे-जैसे मूत्र इस नलिका में प्रभावित होता है इन पदार्थो का चयनित पुनरवशोषण हो जाता है| इस प्रकार से मूत्र का निर्माण गुर्दों में होता है|}
मूत्र का उत्पादन, रुधिर में से अपशिष्ट पदार्थो को छानकर बाहर निकालने से बनता है| नाइट्रोजनी वर्ज्य पदार्थ जैसे यूरिया अथवा यूरिक अम्ल वृक्क में रुधिर से अलग कर लिए जाते हैं| प्रत्येक वृक्क में बहुत से निस्पंदन एकक होते हैं जिन्हें विक्काणु कहते है (जो कि ऊपर चित्र में है)| प्रारंभिक निस्यंद में कुछ पदार्थ, जैसे ग्लूकोज, लवण, अमीनो अम्ल और प्रचुर मात्रा में जल रह जाते है| जैसे-जैसे मूत्र इस नलिका में प्रभावित होता है इन पदार्थो का चयनित पुनरवशोषण हो जाता है| इस प्रकार से मूत्र का निर्माण गुर्दों में होता है|}
Q13. (a) How is protein digestion done in the human body?
(b) Draw a labelled diagram of a nephron (kidney tabules). Description is not required.
(a) मानव के शरीर में प्रोटीन का पाचन कैसे होता है?
(b) एक नेफ्रॉन (वृक्काणु या वृक्क नलिका) का नामांकित चित्र बनाइए| वर्णन की आवश्यकता नहीं है|
Ans. (a) In stomach, gastric glands secrete a protein digesting enzymes called pepsin.
And in the small intestine, pancreas releases pancreatic juice which have enzymes like trypsin for digesting proteins. And small intestine have glands which secrete ‘intestinal juice’. Finally the enzymes present in it convert the proteins to amino acid and this amino acid is absorbed by the wall of the intestine which is called villi.
(b)
{(a) आमाशय में, जठर ग्रंथियाों द्वारा एक प्रोटीन पाचन एंजाइम पेप्प्सिन का स्रावण होता हैं|
और क्षुद्रांत्र में, अग्न्याशय अग्न्याशयिक रस का स्रावण करता हैं जिसमें प्रोटीन के पाचन के लिए ट्रिप्सिन एंजाइम होता है| क्षुद्रांत्र की भित्ति में ग्रंथि होती हैं जो ‘आंत्र रस’ स्रावित करती हैं| इसमें मौजूद एंजाइम अंत में प्रोटीन को अमीनो अम्ल में बदल देते हैं और अमीनो अम्ल को आंत्र की भित्ति अवशोषित कर लेती हैं जिसे दीर्घ रोम कहते हैं|
(b)
}
Q14. Draw a labelled diagram of human digestive system.
{मानव पाचन तंत्र का नामांकित चित्र बनाइए|}
Ans.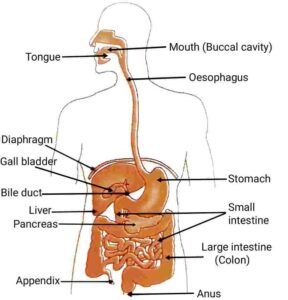
{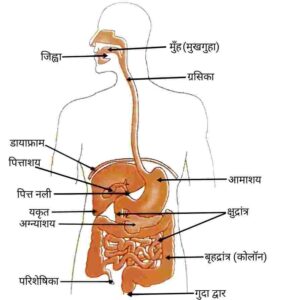 }
}
Q15. (a) What is dialysis?
(b) Draw a labelled diagram of human digestive system.
{(a) अपोहन किसे कहते हैं?
(b) मानव पाचन तंत्र का नामांकित चित्र बनाइए|}
Ans. (a) When our kidney stop working or does not work properly then we use an artificial kidney in this case. Dialysis is a processes in which an artificial kidney is used to remove nitrogenous waste products from the blood.
(b)
{(a)जब हमारी वृक्क काम करना बंद कर देती है या ठीक से काम नहीं करती है तो ऐसे में हम एक कृत्रिम वृक्क का इस्तेमाल करते हैं| अपोहन एक ऐसी प्रक्रिया है जिसमें रक्त से नाइट्रोजनयुक्त अपशिष्ट उत्पादों को निकालने के लिए एक कृत्रिम वृक्क का उपयोग किया जाता है|
(b) }
}
Q16. (a) Draw a labelled diagram of the human excretory system.
(b) Explain the double circulation in human.
{(a) मानव उत्सर्जन तंत्र का नामांकित चित्र बनाइए|
(b) मानव में दोहरे परिसंचरण की व्याख्या कीजिए|}
Ans. (a)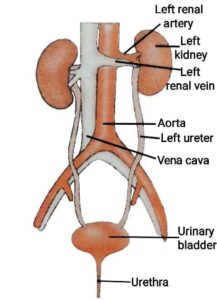
(b) In human beings, blood passes through the heart twice during one circle is known as double circulation.
(1) Oxygenated blood comes from lungs to heart and then heart to all body cells
(2) Deoxygenated blood comes back from the all body cells to heart and then heart to lungs.
{(a)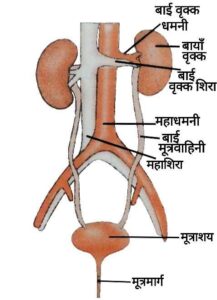
(b) मनुष्य में, रक्त एक चक्र के दौरान दो बार हृदय से होकर गुजरता है, इसे दोहरा परिसंचरण के रूप में जाना जाता है।
(1) ऑक्सीजनित रुधिर फूफ्फस से हृदय और फिर हृदय से शरीर की सभी कोशिकाओं में जाता है|
(2) विऑक्सीजनित रुधिर शरीर की सभी कोशिकाओं से हृदय में और फिर हृदय से फूफ्फस में वापस आ जाता है|}
Q17. (a) Explain the double circulation in human.
(b) What is nutrition? What is the difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic?
{(a) मानव में दोहरे परिसंचरण की व्याख्या कीजिए|
(b) पोषण किसे कहते है? स्वपोषण और परपोषण में क्या अंतर है?}
Ans. (a) In human beings, blood passes through the heart twice during one circle is known as double circulation.
(1) Oxygenated blood comes from lungs to heart and then heart to all body cells
(2) Deoxygenated blood comes back from the all body cells to heart and then heart to lungs.
(b) Nutrition is the process of taking the food and convert it into energy and other nutrients which is required for our body and life.
There are two types of nutrition
(1) Autotrophic nutrition
(2) Heterotrophic nutrition
| Autotrophic | Heterotrophic |
| (1) Those organisms which makes their own food are called autotrophs and such type of nutrition is called autotrophic nutrition. | (1) Those organisms which is depended directly or indirectly on the autotrophs and such type of nutrition is called heterotrophic nutrition. |
| (2) Ex:- Plant, tree, some bacterias. | (2) Ex:- +Human beings, animals, fishes etc. |
{(a) मनुष्य में, रक्त एक चक्र के दौरान दो बार हृदय से होकर गुजरता है, इसे दोहरा परिसंचरण के रूप में जाना जाता है।
(1) ऑक्सीजनित रुधिर फूफ्फस से हृदय और फिर हृदय से शरीर की सभी कोशिकाओं में जाता है|
(2) विऑक्सीजनित रुधिर शरीर की सभी कोशिकाओं से हृदय में और फिर हृदय से फूफ्फस में वापस आ जाता है|}
(b) पोषण भोजन को लेने और उसे ऊर्जा और अन्य पोषक तत्वों में परिवर्तित करने की प्रक्रिया है जो हमारे शरीर और जीवन के लिए आवश्यक है|
पोषण दो प्रकार का होता है
(1) स्वपोषण
(2) परपोषण
| स्वपोषण | परपोषण |
| (1) वे जीव जो अपना भोजन स्वयं बनाते हैं स्वपोषी कहलाते हैं और इस प्रकार के पोषण को स्वपोषण कहते हैं| | (1) वे जीव जो प्रत्यक्ष या परोक्ष रूप से स्वपोषी पर निर्भर होते हैं और इस प्रकार के पोषण परपोषण कहलाते हैं| |
| (2) उदाहरण:- पौधे, पेड़, कुछ जीवाणु| | (2) उदाहरण:- मनुष्य, पशु, मछलियाँ आदि| |
}
Q18. (a) What is the benefit to human heart having four chambers?
(b) How does oxygen reach to tissues from lungs?
(क) मानव हृदय में चार कोष्ठों के होने से क्या लाभ है?
(ख) ऑक्सीजन फेफड़े से ऊत्तकों तक कैसे पहुँचती है?
Ans. (a) Human heart have four chambers because both carbon dioxide and oxygen have to be transported by the blood and this chambers prevent the mixing of oxygen-rich blood with the blood having carbon dioxide. Such separation allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the whole body. This is useful for high energy requirements.
(b) The blood vessels carry oxygen from alveoli of lungs. Then oxygen-rich blood from the lungs reaches to the upper left chamber of the heart, called the left atrium. The left atrium relaxes when it is collecting this blood. Then it contracts, while the left ventricle relaxes. So that the blood is transferred to it. When the left ventricles contracts, the blood is pumped out to the various parts of the body. This is the process of oxygen reach to tissues from lungs.
{(a) मानव हृदय चार कोष्ठो में बँटा होता हैं क्योंकि रुधिर को ऑक्सीजन व कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड दोनों का ही वहन करना होता है और यह कोष्ठ ऑक्सीजन प्रचुर रुधिर को कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड युक्त रुधिर से मिलने से रोकते है| इस तरह का बँटवारा शरीर को उच्च दक्षतापूर्ण ऑक्सीजन की पूर्ति करता है| उच्च ऊर्जा की जरूरत के लिए के लिए यह बहुत उपयोगी होती है|
(b) रुधिर वाहिकाएंँ फेफड़ों की कूपिका से ऑक्सीजन ले जाती हैं| ऑक्सीजन प्रचुर रुधिर फेफड़ों से हृदय में बाई ओर स्थित कोष्ठ-बायाँ आलिंद में आता है| इस रुधिर को इकट्ठा करते समय बायां आलिंद शिथिल रहता है| जब अगला कोष्ठ (बायाँ निलय) फैलता है तब यह संकुचित होता है जिससे रुधिर इसमें स्थानांतरित होता है| अपनी बारी पर जब पेशीय बायाँ निलय संकुचित होता है, तब रुधिर शरीर में पम्पित हो जाता हैं| यह प्रक्रिया से ऑक्सीजन फेफड़े से ऊतकों तक पहुँचती है|}
Q19. (a) What will be the effect on our body due to haemoglobin deficiency? Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals?
(b) Draw a diagram of a human heart and label it parts.
{(a) हीमोग्लोबिन हीनता के कारण हमारे शरीर पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ेगा? स्तनधारियों में ऑक्सीजनित और विऑक्सीजनित रुधिर को पृथक करना क्यों आवश्यक है?
(b) हृदय के परिच्छेद दृश्य का चित्र बनाकर उसके भागों का नाम लिखिए|}
Ans. (a) When haemoglobin level will decrease in our body then blood could not be able to transport proper amount of oxygen to all our body cells. This cause deficiency of oxygen in our body or body’s cells which result as improper digestion.
It is necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals because such separation allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the whole body. This is useful for high energy requirements in mammals which constantly used this energy to maintain their body temperature.
(b)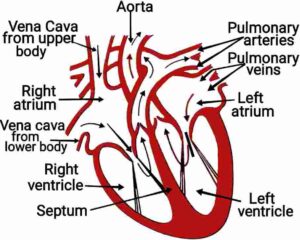
{(a) जब हमारे शरीर में हीमोग्लोबिन का स्तर कम हो जाएगा तो रक्त हमारे शरीर की सभी कोशिकाओं तक उचित मात्रा में ऑक्सीजन नहीं पहुंचा पाएगा| यह हमारे शरीर या शरीर की कोशिकाओं में ऑक्सीजन की कमी का कारण बनता है जिसके परिणामस्वरूप अनुचित पाचन होता है|
स्तनधारियों में ऑक्सीजनित और विऑक्सीजनित रुधिर को अलग करना आवश्यक है क्योंकि इस तरह का बँटवारा से पूरे शरीर को ऑक्सीजन की अत्यधिक कुशल आपूर्ति होती है| यह स्तनधारियों में उच्च ऊर्जा आवश्यकताओं के लिए उपयोगी है जो लगातार इस ऊर्जा का उपयोग अपने शरीर के तापमान को बनाए रखने के लिए करते हैं|
(b)  }
}
9113323460

I hope you like it. If you like then please share it and you can also Donate to our website by my number and QR code which is given above.
Thanks.
Next Chapter Control and Coordination (नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय)
Control and Coordination (नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय)
