Carbon and its Compounds (कार्बन एवं उसके यौगिक)
Get “Carbon and its Compounds” chapter’s previous years questions from 2009 to 2020 of JAC board.
Q1. Which hydrocarbon group has general formula ?
{ किस हाइड्रोकार्बन समूह का सामान्य सूत्र है|}
Ans. Alkenes
{ऐल्कीनों}
Q2. What is the general formula of alkyne?
{ऐल्काइन का सामान्य सूत्र क्या है?}
Ans.
Q3. What is the general formula of alkane?
{ऐल्केन का सामान्य सूत्र क्या है?}
Ans.
Q4. What is the general formula of alkenes?
{एल्कीन्स का सामान्य सूत्र क्या है?}
Ans.
Q5. Name the functional group .
{प्रकार्यात्मक समूह का नाम बताइए|}
Ans. Carboxylic acid
{कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल}
Q6. Identify the functional group present in .
{ में मौजूद प्रकार्यात्मक समूह की पहचान करें|}
Ans. Ketone
{कीटोन}
Q7. What is the functional group of butanone?
{ब्यूटेनॉन का प्रकार्यात्मक समूह क्या है?}
Ans. Ketone
{कीटोन}
Q8. Which of the following is an aldehyde?
{निम्नलिखित में से कौन एक एल्डिहाइड है?}
Ans. HCHO
Q9. Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions
and
{हाइड्रोकार्बन
एवं
में से किसमें संकलन अभिक्रिया होती है?}
Ans.
Q10. An organic compound burns with a sooty flame. Is it is saturated or unsaturated compound?
{एक कार्बनिक यौगिक कालिख ज्वाला के साथ जलता है| क्या यह संतृप्त यौगिक है या असंतृप्त?}
Ans. Unsaturated compound
{असंतृप्त यौगिक}
Q11. Write two differences between soap and detergent.
{साबुन और अपमार्जक में दो अंतर लिखिए|}
Ans.
| Soap | Detergent |
| (1) The molecules of soaps are potassium or sodium salts of long-chain carboxylic acid. | (1) The molecules of detergent are sulphonate or ammonium salts of long chain carboxylic acid. |
| (2) In hard water, soap reacts with magnesium and calcium salt and produce scum(precipitates). | (2) In hard water, detergent do not produce insoluble precipitates with magnesium and calcium salt. |
{
| साबुन | अपमार्जक |
| (1) साबुन के अणु लंबी श्रृंखला वाले कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्लों के पोटैशियम या सोडियम लवण होते हैं| | (1) अपमार्जक के अणु लम्बी कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल श्रृंखला के सल्फोनेट या अमोनियम लवण होते हैं| |
| (2) In hard water, soap reacts with magnesium and calcium salt and produce scum(precipitates). | (2) कठोर जल में, डिटर्जेंट मैग्नीशियम और कैल्शियम लवण के साथ अघुलनशील अवक्षेप नहीं बनाता है| |
}
Q12. What is homologous series? Explain with an example.
{समजातीय श्रेणी क्या है? उदाहरण सहित समझाइए|}
Ans. Homologous series are a series of carbon compound which have a different number of carbon atoms and they contain the same functional group. The chemical properties of all compounds in a homologous series are identical and difference between any successive compound are .
For ex:- Homologous series of alkenes is .
In here, the chemical properties of all compounds of alkenes are identical and the difference between their successive compound are .
{समजातीय श्रेणी कार्बन यौगिकों की एक श्रृंखला है जिसमें अलग-अलग संख्या वाले कार्बन परमाणुओं होते है और उनमें एक ही कार्यात्मक समूह होता है| एक समजातीय श्रेणी के सभी यौगिकों के रासायनिक गुण समान होते हैं और किसी भी क्रमागत यौगिक के बीच का अंतर होता है|
उदाहरण के लिए:- ऐल्कीनों की समजातीय श्रृंखला है|
यहाँ ऐल्कीनों की सभी यौगिकों के रासायनिक गुण समान होते हैं और उनके क्रमागत यौगिकों के बीच का अंतर होता है|}
Q13. Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid called as oxidation reaction?
{एथेनॉल से एथेनॉइक अम्ल में परिवर्तन को ऑक्सीकरण अभिक्रिया क्यों कहते हैं?}
Ans.
Alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate are oxidising agent which oxidising alcohol to acid. In this reaction, hydrogen is removed from ethanol and oxygen is added to ethanoic acid. Thus, the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid called as oxidation reaction.
{ क्षारीय पोटेशियम परमैंगनेट या अम्लीकृत पोटेशियम डाइक्रोमेट ऑक्सीकारक एजेंट हैं जो ऐल्कोहॉलों को अम्लों में ऑक्सीकृत करते हैं| इस अभिक्रिया में एथेनॉल से हाइड्रोजन हट जाता है और ऑक्सीजन एथेनॉइक अम्ल में मिल जाता है| इस प्रकार एथेनॉल का एथेनोइक अम्ल में परिवर्तन ऑक्सीकरण अभिक्रिया कहलाता है|}
क्षारीय पोटेशियम परमैंगनेट या अम्लीकृत पोटेशियम डाइक्रोमेट ऑक्सीकारक एजेंट हैं जो ऐल्कोहॉलों को अम्लों में ऑक्सीकृत करते हैं| इस अभिक्रिया में एथेनॉल से हाइड्रोजन हट जाता है और ऑक्सीजन एथेनॉइक अम्ल में मिल जाता है| इस प्रकार एथेनॉल का एथेनोइक अम्ल में परिवर्तन ऑक्सीकरण अभिक्रिया कहलाता है|}
Q14. What do you mean by addition and substitution reactions? Give one example of each of the two.
{संकलन और प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया से आप क्या समझते हैं? दोनों में प्रत्येक के एक-एक उदाहरण दीजिए|}
Ans. Addition reaction:- Those reaction in which a molecule is added to an unsaturated compounds to form a single product are called addition reaction.
For ex:- Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the presence of catalysts like nickel or palladium to produce saturated hydrocarbons.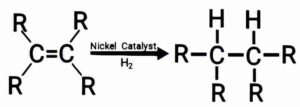
Substitution reaction:- Those reaction in which one kind of atom or group of atoms in a carbon compound is replaced by another atom or group of atoms are called substitution reactions.
For ex:- Chlorine is added to hydrocarbons in the presence of sunlight in a very fast reaction.
(In the presence of sunlight)
{संकलन अभिक्रिया:- वे अभिक्रिया जिनमें एक अणु को असंतृप्त यौगिकों में मिलाकर एकल उत्पाद बनाया जाता है, संकलन अभिक्रिया है|
उदाहरण:- निकेल या पैलेडियम जैसे उत्प्रेरकों की उपस्थिति में असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन हाइड्रोजन जोड़कर संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन बना देते हैं|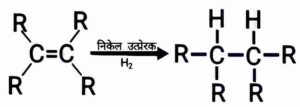
प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया:- वे अभिक्रियाएँ जिनमें कार्बन यौगिक में एक प्रकार के परमाणु या परमाणुओं के समूह को दूसरे परमाणु या परमाणुओं के समूह द्वारा प्रतिस्थापित किया जाता है, प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया कहलाती हैं|
उदाहरण:- सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में बहुत तेज अभिक्रिया में क्लोरीन का हाइड्रोकार्बन में संकलन होता है|
(सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में) }
Q15. Write the I.U.P.A.C name of the following compounds:
{निम्नलिखित यौगिकों के I.U.P.A.C नाम लिखिए:}
Ans. (a) Methanoic acid
(b) Methanal
(c) Butanone
{(a) मेथेनॉइक अम्ल
(b) मेथेनैल
(c) ब्यूटेनोन}
Q16. Write the structural formula of the following organic compounds:
(a) Acetylene
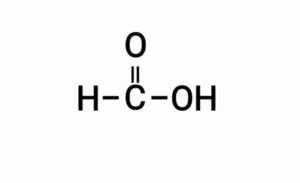
(b) Formic acid
(c) Methyl alcohol
{निम्नलिखित कार्बनिक यौगिकों का संरचना सूत्र लिखिए:
(a) ऐसीटिलीन
(b) फॉर्मिक अम्ल
(c) मेथाइल ऐल्कोहॉल}
Ans. (a) Acetylene
{ऐसीटिलीन}
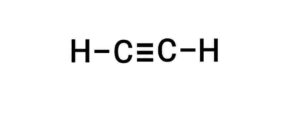 (b) Formic acid
(b) Formic acid
{फॉर्मिक अम्ल}
(c) Methyl alcohol
{मेथाइल ऐल्कोहॉल}
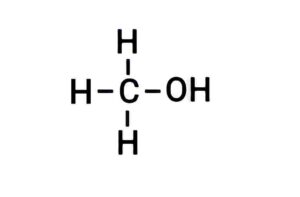
Q17. Write the structural formula of the following compounds:
(a) Ethanol
(b) Ethanoic acid
(c) Methanal
{निम्नलिखित यौगिकों का संरचना सूत्र लिखिए:
(a) इथेनॉल
(b) इथेनोइक अम्ल
(c) मेथेनैल }
Ans. (a) Ethanol
{इथेनॉल}
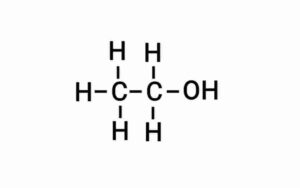
(b) Ethanoic acid
{इथेनोइक अम्ल}
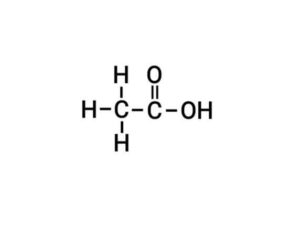
(c) Methanal
{मेथेनैल}
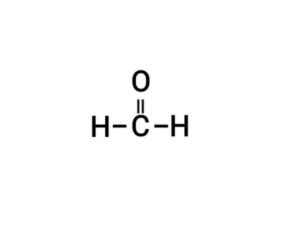
Q18. Write the structural formula of the following compounds:
(a) Ethene
(b) Propane
(c) Chlorobutane
{निम्नलिखित यौगिकों का संरचना सूत्र लिखिए:
(a) इथीन
(b) प्रोपेन
(c) क्लोरोब्यूटेन}
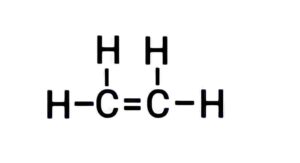
Ans. (a) Ethane
{इथीन}
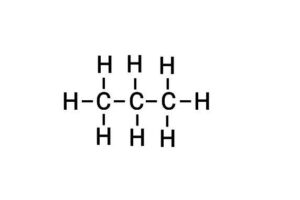
(b) Propane
{प्रोपेन}
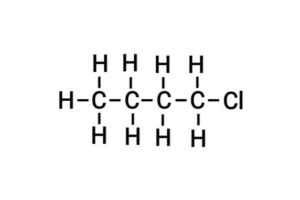
 (c) Chlorobutane
(c) Chlorobutane
{क्लोरोब्यूटेन}
Q19. Write any two differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
{संतृप्त और असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन में कोई दो अंतर लिखिए|}
Ans.
| Saturated hydrocarbons | Unsaturated hydrocarbons |
| (1) The carbon compounds which contain only single bond between the two carbon atoms are called saturated hydrocarbon. | (1) The carbon compound which contain double or triple bonds between two carbon atoms are called unsaturated hydrocarbon. |
| (2) These compounds are generally non reactive. | (2)These compounds are highly reactive in comparison to the saturated hydrocarbon. |
{
| संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन | असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन |
| (1) वे कार्बन यौगिक जिनमें दो कार्बन परमाणुओं के बीच केवल एक ही आबंधन हो, उसे संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन कहते हैं| | (1) वे कार्बन यौगिक जिनमें दो कार्बन परमाणुओं के बीच द्वि या त्रि आबंधन हो, उसे असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन कहते हैं| |
| (2) ये यौगिक आम तौर पर कम अभीक्रियाशील होते हैं| | (2) ये यौगिक संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन की तुलना में अत्यधिक अभीक्रियाशील होते हैं| |
}
Q20. Fill in the blanks
| Compound | IUPAC name | Present functional group |
| Ethanol | ||
{रिक्त स्थान भरें
| यौगिक | IUPAC नाम | उपस्थित प्रकार्यात्मक समूह |
| इथेनॉल | ||
}
Ans. (a) Methanal, Aldehyde group
(b) , Alcohol group
(c) 2-chloropropene, Halogen group
{(a) मेथेनैल, ऐल्डिहाइड समूह
(b) , ऐल्कोहॉल समूह
(c) 2-क्लोरोप्रोपीन, हैलोजन समूह}
Q21. (a) How is ethene made from ethanol?
(b) How is an ester made from ethanoic acid?
{(a) एथनॉल से इथीन कैसे बनता है?
(b) एथेनॉइक अम्ल से एस्टर कैसे बनता है?}
Ans. (a) When heating ethanol with excess concentrated sulphuric acid at 443K then ethanol dehydrate and ethene is formed.
(b) Ethanoic acid combined with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst to produce an easter.
{(a) 443K तापमान पर एथनॉल को आधिक्य सान्द्र सल्फ्यूरिक अम्ल के साथ गर्म करने पर एथनॉल का निर्जलीकरण हो जाता है और यह एथीन बन जता है|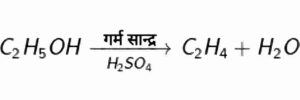
(b) एथेनॉइक अम्ल किसी अम्ल उत्प्रेरक की उपस्थिति में एथनॉल से अभिक्रिया करके एस्टर बना देता है|
}
Q22. What is alkyne? Write their general formula. Write the name and electronic structure of simplest alkyne.
{एल्काइन क्या है? उनका सामान्य सूत्र लिखिए। सबसे सरल एल्काइन का नाम तथा इलेक्ट्रॉनिक संरचना लिखिए|}
Ans. The unsaturated hydrocarbons which have one or more triple bonds are known as alkynes.
The general formula of alkynes is .
Ethyne is the simplest alkyne.
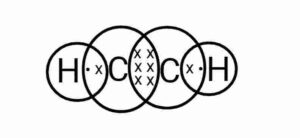
{वे असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन जिनमें एक या एक से अधिक त्रि-आबंध होते हैं, उसे उसे एल्काइन कहते हैं|
एल्काइन का सामान्य सूत्र है|
इथाइन सबसे सरल ऐल्काइन है|
 }
}
Q23. Name the following compounds:-
(a) An alcohol derived from ethane
(b) An ketone derived from butane
(c) An carboxylic acid derived from methane
{निम्नलिखित यौगिकों के नाम लिखिए:-
(a) एथेन से व्युत्पन्न एक ऐल्कोहॉल
(b) ब्यूटेन से व्युत्पन्न एक कीटोन
(c) मेथेन से व्युत्पन्न एक कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल}
Ans. (a) Ethanol
(b) Butanone
(c) Methanoic acid
{(a) एथेनॉल
(b) ब्यूटेनोन
(c) मेथेनोइक अम्ल}
Q24. What is isomerism? Write the names and structural formula of the isomers of pentane.
{समावयवता किसे कहते है? पेंटेन के समावयवों के नाम और संरचनात्मक सूत्र लिखिए|}
Ans. The phenomenon that two or more different chemical compounds have the same molecular formula is called isomerism.
There are 3 structural isomers of pentane.
(a) n-pentane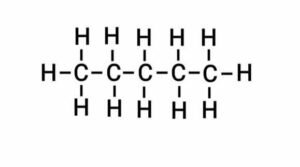
(b) Iso-pentane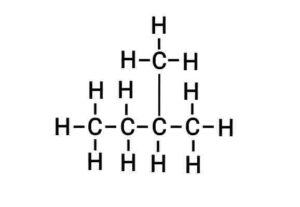
(c) Neo-pentane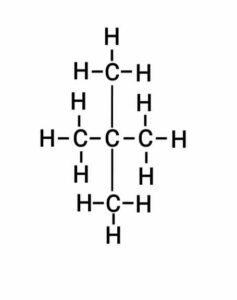
{दो या दो से अधिक विभिन्न रासायनिक यौगिकों के समान आणविक सूत्र होने की घटना को समावयवता कहा जाता है|
पेंटेन के 3 संरचनात्मक समावयन होते हैं|
(a) एन-पेंटेन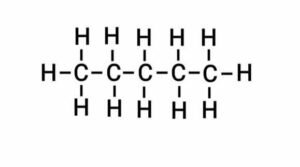
(b) आइसो-पेंटेन
(c) नियो-पेंटेन }
}
Q25. Write the structural formula of the following compounds:
(a) Ethanoic acid
(b) Bromopentane
(c) Butanone
(d) Hexanal
(e) Propanol
{निम्नलिखित यौगिकों का संरचना सूत्र लिखिए:
(a) इथेनोइक अम्ल
(b) ब्रोमोपेंटेन
(c) ब्यूटेनोन
(d) हेक्सेनैल
(e) प्रोपेनॉल}
Ans. (a) Ethanoic acid
{इथेनोइक अम्ल}

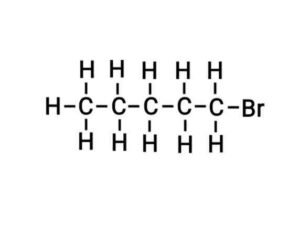
(b) Bromopentane
{ब्रोमोपेंटेन}
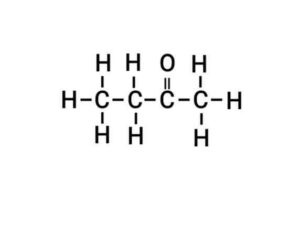
(c) Butanone
{ब्यूटेनोन}
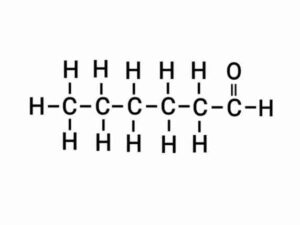
(d) Hexanal
{हेक्सेनैल}
(e) Propanol
{प्रोपेनॉल}
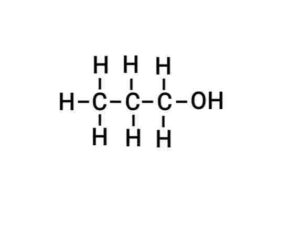
Q26. (a) Give three main reasons for the formation of compounds with a large numbers of carbons.
(b) Write the structural formula of ethanol and ethanoic acid
{(a) कार्बन के अत्यधिक संख्या से यौगिकों के निर्माण का प्रमुख तीन कारण दीजिए|
(b) इथेनॉल और इथेनोइक अम्ल का संरचना सूत्र लिखिए|}
Ans. (a) The reasons for the formation of compounds with a large numbers of carbons:-
(1) Catenation:- Carbon has the unique capability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon which giving rise to large molecules. These carbon compounds may have long chains, branched, ring, single bond, double bond and triple bond.
(2) Tetravalency:- Since valency of carbon is 4. So it is capable to bonding with four other atoms of carbon or some other elements.
(3) The carbon-carbon bond is very strong and stable bond because carbon has small size. Due to small size of carbon, the nucleus able to hold on the shared pair of electrons strongly. This is the reason for the formation of compound with a large number of carbon.
(b) Ethanol

Ethanoic acid

{(a) कार्बन के अत्यधिक संख्या से यौगिकों के निर्माण का कारण:-
(1) श्रृंखलन :- कार्बन में कार्बन के ही अन्य परमाणुओं के साथ आबंध बनाने की अनोखी क्षमता होती है, जिससे बड़े अणु बनते है। इन कार्बन यौगिकों में लंबी श्रृंखला, शाखाएं, वलय, एक आबंध, द्वि आबंध और त्रि आबंध हो सकते हैं|
(2) चतुः संयोजकता:- चूंकि कार्बन की संयोजकता 4 होती है, इसलिए यह कार्बन के चार अन्य परमाणुओं या किसी अन्य तत्वों के साथ आबंध करने में सक्षम हैं|
(3) कार्बन-कार्बन आबंधन बहुत मजबूत और स्थिर आबंधन होता है क्योंकि कार्बन का आकार छोटा होता है| कार्बन के छोटे आकार के कारण, इलेक्ट्रॉन के सहभागी जोड़ों को नाभिक मजबूती से बाँधे रहता है| यही कार्बन के अत्यधिक संख्या से यौगिकों के निर्माण का कारण है|
(b) इथेनॉल

(b) इथेनोइक अम्ल
 }
}
Q27. (a) What is homologous series? Explain with an example.
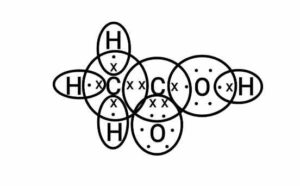
(b) Draw the electronic dot structure of the following.
(i) Ethanoic acid
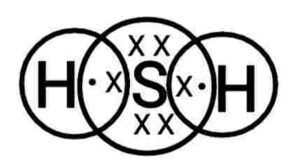
(ii)
(iii) Propanone
{(a) समजातीय श्रेणी क्या है? उदाहरण सहित समझाइए|
(b) निम्न का इलेक्ट्रॉनिक बिन्दु संरचना बनाएं|
(i) एथेनॉइक अम्ल
(ii)
(iii) प्रोपेनोन}
Ans. (a) Homologous series are a series of carbon compound which have a different number of carbon atoms and they contain the same functional group. The chemical properties of all compounds in a homologous series are identical and difference between any successive compound are .
For ex:- Homologous series of alkenes is .
In here, the chemical properties of all compounds of alkenes are identical and the difference between their successive compound are .
(b) (i) Ethanoic acid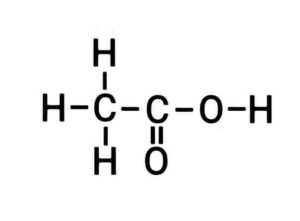
 (ii)
(ii) 
 (iii) Propanone
(iii) Propanone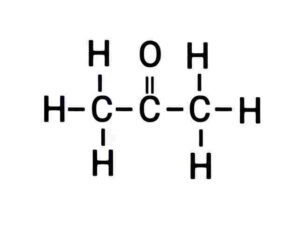
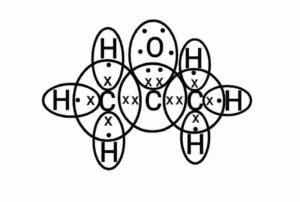
{समजातीय श्रेणी कार्बन यौगिकों की एक श्रृंखला है जिसमें अलग-अलग संख्या वाले कार्बन परमाणुओं होते है और उनमें एक ही कार्यात्मक समूह होता है| एक समजातीय श्रेणी के सभी यौगिकों के रासायनिक गुण समान होते हैं और किसी भी क्रमागत यौगिक के बीच का अंतर होता है|
उदाहरण के लिए:- ऐल्कीनों की समजातीय श्रृंखला है|
यहाँ ऐल्कीनों की सभी यौगिकों के रासायनिक गुण समान होते हैं और उनके क्रमागत यौगिकों के बीच का अंतर होता है|}
(b) (i) एथेनॉइक अम्ल
 (ii)
(ii) 
 (iii) प्रोपेनोन
(iii) प्रोपेनोन

}
Q28. (a) What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we around us.
(b) Write three differences between soap and detergent.
{(a) कार्बन के दो गुणधर्म कौन-से हैं, जिनके कारण हमारे चारों ओर कार्बन यौगिकों की बड़ी संख्या दिखाई देती है?
(b) साबुन और अपमार्जक में तीन अंतर लिखिए|}
Ans. (a) The two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we around us are:-
Catenation:- Carbon has the unique capability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon which giving rise to large molecules. These carbon compounds may have long chains, branched, ring, single bond, double bond and triple bond.
Tetravalency:- Since valency of carbon is 4. So it is capable to bonding with four other atoms of carbon or some other elements.
(b)
| Soap | Detergent |
| (1) The molecules of soaps are potassium or sodium salts of long-chain carboxylic acid. | (1) The molecules of detergent are sulphonate or ammonium salts of long chain carboxylic acid. |
| (2) In hard water, soap reacts with magnesium and calcium salt and produce scum(precipitates). | (2) In hard water, detergent do not produce insoluble precipitates with magnesium and calcium salt. |
| (3) It is easily biodegradable. | (3) It is non biodegradable. |
{(a) कार्बन के दो गुणधर्म जिनके कारण हमारे चारों ओर कार्बन यौगिकों की बड़ी संख्या दिखाई देती है:-
श्रृंखलन :- कार्बन में कार्बन के ही अन्य परमाणुओं के साथ आबंध बनाने की अनोखी क्षमता होती है, जिससे बड़े अणु बनते है। इन कार्बन यौगिकों में लंबी श्रृंखला, शाखाएँ, वलय, एक आबंध, द्वि आबंध और त्रि आबंध हो सकते हैं|
चतुः संयोजकता:- चूंकि कार्बन की संयोजकता 4 होती है, इसलिए यह कार्बन के चार अन्य परमाणुओं या किसी अन्य तत्वों के साथ आबंध करने में सक्षम हैं|
(b)
| साबुन | अपमार्जक |
| (1) साबुन के अणु लंबी श्रृंखला वाले कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्लों के पोटैशियम या सोडियम लवण होते हैं| | (1) अपमार्जक के अणु लम्बी कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल श्रृंखला के सल्फोनेट या अमोनियम लवण होते हैं| |
| (2) कठोर जल में साबुन मैग्नीशियम तथा कैल्सियम लवण के साथ अभिक्रिया करके स्कम(अवक्षेप) उत्पन्न करता है| | (2) कठोर जल में, डिटर्जेंट मैग्नीशियम और कैल्शियम लवण के साथ अघुलनशील अवक्षेप नहीं बनाता है| |
| (3) यह आसानी से जैव निम्नीकरणीय हो जाते है| | (3) यह जैव निम्नीकरणीय नहीं होते है| |
}
Q29. (a) What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
(b) Explain with figure the mechanism of the cleaning action of soap.
{(a) हाइड्रोजनीकरण क्या है? इसका औद्योगिक अनुप्रयोग क्या है?
(b) साबुन की सफाई प्रक्रिया की क्रियाविधि सचित्र समझाइए|}
Ans. (a) Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the presence of catalysts like nickel or palladium to produce saturated hydrocarbons. This reaction is called hydrogenation.
This reaction is generally used in the hydrogenation of vegetable oils using a nickel catalyst. Vegetable oils (usually contain long unsaturated carbon chain) is used to making butter and ghee (contain saturated hydrocarbons).
(b) Most dirt have oily nature and oil is not soluble in water. The molecules of soap are potassium or sodium salts of long-chain carboxylic acid. The ionic end of soap dissolves in water while the carbon chain is soluble in oil. The soap molecules thus produce structure called micelles, where one end of the molecules faces the oil droplet while the acid end is towards outside. This produces an emulsion in water. The soap micelles thus helps in dissolving the dirt in water and we can cleanly wash our cloths.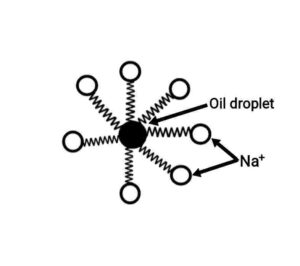
{(a) पैलेडियम या निकेल जैसे उत्प्रेरकों की उपस्थिति में असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन हाइड्रोजन जोड़कर संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन बना देता है| इस अभिक्रिया को हाइड्रोजनीकरण कहा जाता है।
यह अभिक्रिया आमतौर पर निकेल उत्प्रेरक का उपयोग करके वनस्पति तेलों के हाइड्रोजनीकरण में उपयोग की जाती है| वनस्पति तेलों (जिसमे प्रायः लंबी असंतृप्त कार्बन श्रृंखलाएँ होती है) का उपयोग करके हम मक्खन और घी बनाते हैं (जो की संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन होते हैं|)
(b) अधिकांश मैल तैलीय प्रकृति के होते है और तेल पानी में घुलनशील नहीं होता है| साबुन के अणु लंबी-श्रृंखला वाले कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल के पोटैशियम या सोडियम लवण होते हैं| साबुन का आयनिक भाग पानी में घुल जाता है जबकि कार्बन श्रृंखला तेल में घुल जाती है| इस प्रकार साबुन के अणु मिसेली संरचना तैयार करते हैं, जहाँ अणुओं का एक सिरा तेल कण की तरफ और आयनिक सिरा बाहर की तरफ होता है| इससे पानी में एक इमल्शन बनता है| इस प्रकार साबुन का मिसेल मैल को पानी में घुलाने में मदद करता हैं और हमारे कपड़े साफ हो जाते हैं|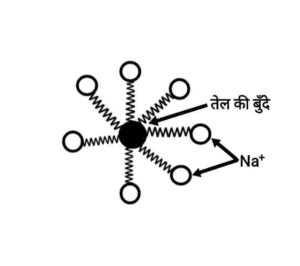 }
}
Q30. (a) Write any two differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
(b) Give one example each of the above two types of hydrocarbons.
(c) Whether the compound is saturated or unsaturated? Why?
{(a) संतृप्त और असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन में कोई दो अंतर लिखिए|
(b) उपरोक्त दोनों प्रकार के हाइड्रोकार्बनो का एक-एक उदाहरण दें|
(c) यौगिक संतृप्त है या असंतृप्त? क्यों?}
Ans. (a)
| Saturated hydrocarbons | Unsaturated hydrocarbons |
| (1) The carbon compounds which contain only single bond between the two carbon atoms are called saturated hydrocarbon. | (1) The carbon compound which contain double or triple bonds between two carbon atoms are called unsaturated hydrocarbon. |
| (2) These compounds are generally non reactive. | (2)These compounds are highly reactive in comparison to the saturated hydrocarbon. |
(b) Saturated hydrocarbons-
Unsaturated hydrocarbons-
(c) Unsaturated hydrocarbons
{
| संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन | असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन |
| (1) वे कार्बन यौगिक जिनमें दो कार्बन परमाणुओं के बीच केवल एक ही आबंधन हो, उसे संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन कहते हैं| | (1) वे कार्बन यौगिक जिनमें दो कार्बन परमाणुओं के बीच द्वि या त्रि आबंधन हो, उसे असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन कहते हैं| |
| (2) ये यौगिक आम तौर पर कम अभीक्रियाशील होते हैं| | (2) ये यौगिक संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन की तुलना में अत्यधिक अभीक्रियाशील होते हैं| |
(b) संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन- मीथेन
असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन- एथेन
(c) असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन}
Q31. (a) What do you mean by addition and substitution reactions? Give one example of each of the two.
(b) What is the industrial application of hydrogenation?
{(a) संकलन और प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया से आप क्या समझते हैं? दोनों में प्रत्येक के एक-एक उदाहरण दीजिए|
(b) हाइड्रोजनीकरण का औद्योगिक अनुप्रयोग क्या है?}
Ans. (a) Addition reaction:- Those reaction in which a molecule is added to an unsaturated compounds to form a single product are called addition reaction.
For ex:- Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the presence of catalysts like nickel or palladium to produce saturated hydrocarbons.
Substitution reaction:- Those reaction in which one kind of atom or group of atoms in a carbon compound is replaced by another atom or group of atoms are called substitution reactions.
For ex:- Chlorine is added to hydrocarbons in the presence of sunlight in a very fast reaction.
(In the presence of sunlight)
(b) This reaction is generally used in the hydrogenation of vegetable oils using a nickel catalyst. Vegetable oils (usually contain long unsaturated carbon chain) is used to making butter and ghee (contain saturated hydrocarbons).
{संकलन अभिक्रिया:- वे अभिक्रिया जिनमें एक अणु को असंतृप्त यौगिकों में मिलाकर एकल उत्पाद बनाया जाता है, संकलन अभिक्रिया है|
उदाहरण:- निकेल या पैलेडियम जैसे उत्प्रेरकों की उपस्थिति में असंतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन हाइड्रोजन जोड़कर संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन बना देते हैं|
प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया:- वे अभिक्रियाएँ जिनमें कार्बन यौगिक में एक प्रकार के परमाणु या परमाणुओं के समूह को दूसरे परमाणु या परमाणुओं के समूह द्वारा प्रतिस्थापित किया जाता है, प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया कहलाती हैं|
उदाहरण:- सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में बहुत तेज अभिक्रिया में क्लोरीन का हाइड्रोकार्बन में संकलन होता है|
(सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में)
(b) यह अभिक्रिया आमतौर पर निकल उत्प्रेरक का उपयोग करके वनस्पति तेलों के हाइड्रोजनीकरण में उपयोग की जाती है| वनस्पति तेलों (जिसमे प्रायः लंबी असंतृप्त कार्बन श्रृंखलाएँ होती है) का उपयोग करके हम मक्खन और घी बनाते हैं (जो की संतृप्त हाइड्रोकार्बन होते|)}
Q32. (i) Label (1) and (2) in the given figure.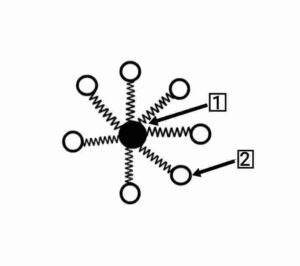 (ii) To know whether a sample of water is hard or soft – which one would you choose between soap and detergent and why?
(ii) To know whether a sample of water is hard or soft – which one would you choose between soap and detergent and why?
(iii) Which catalyst is used in hydrogenation?
{(i) दिए गए चित्र में (1) और (2) को नामांकित करें| (ii) जल का कोई नमूना कठोर है या मृदु – यह जानने के लिए आप साबुन और डिटरजेंट में किसका चुनाव करेंगे और क्यों?
(ii) जल का कोई नमूना कठोर है या मृदु – यह जानने के लिए आप साबुन और डिटरजेंट में किसका चुनाव करेंगे और क्यों?
(iii) हाइड्रोजनीकरण में किस उत्प्रेरक का उपयोग किया जाता है?
Ans. (i) 1. Oil droplet
2.
(ii) Soap
In hard water, when we use soap then it is difficult to produced foam and an insoluble substance (scum) remains behind after washing with water. So we use larger amount of soap. But this problem does not happen in the case of detergent. Detergent are effective in hard water and do not produce insoluble precipitates. So by the help of soap we can recognise that the given sample of water is soft or hard.
(iii) Nickel
{(i) 1. तेल की बूंद
2.
(ii) साबुन
कठोर जल में जब हम साबुन का प्रयोग करते हैं तो झाग उत्पन्न करना कठिन हो जाता है तथा जल से धोने के बाद अघुलनशील पदार्थ(मैल) रह जाता है| इसलिए हम अधिक मात्रा में साबुन का उपयोग करते हैं| लेकिन डिटर्जेंट के मामले में यह समस्या नहीं होती है| अपमार्जक कठोर जल में प्रभावी होते हैं और अघुलनशील अवक्षेप उत्पन्न नहीं करते हैं| अतः साबुन की सहायता से हम पहचान सकते हैं कि दिया गया पानी का नमूना कठोर है या मृदु है|
(iii) निकेल}
Q33. An organic compound A is widely used as a preservative in pickles and has molecular formula . This compound reacts with ethanol to form a sweet smelling compound B
(i) Identify the compound A
(ii) Write the chemical equation for its reaction with ethanol to form a compound B
(iii) How can you get back compound A from compound B
(iv) Name the process and write the corresponding chemical equation.
{एक कार्बनिक यौगिक A अचारों में परिरक्षक के रूप में उपयोग होता है और इसका अणुसूत्र हैं| यह यौगिक एथेनॉल से अभिक्रिया करके एक मीठा महक वाला यौगिक B बनाता है|
(i) यौगिक A की पहचान करें|
(ii) यौगिक B बनाने के लिए इसकी एथेनॉल से अभिक्रिया के लिए रासायनिक समीकरण लिखिए|
(iii) यौगिक B, यौगिक A से वापस कैसे मिल सकता है?
(iv) प्रक्रिया का नाम तथा संगत समीकरण लिखें|}
Ans. (i) Ethanoic acid
(ii)
(iii) By hydrolysis of ester, we can get back compound A from compound B. Ester react in the presence of an acid or a base to produce back the ethanoic acid and ethanol.
(iv) Process – Saponification
{(i) एथेनॉइक अम्ल
(ii)
(iii) एस्टर के जल अपघटन द्वारा, हम यौगिक B से यौगिक A वापस प्राप्त कर सकते हैं| एस्टर अम्ल या क्षारक की उपस्थिति में अभिक्रिया करके वापिस एथेनॉइक अम्ल और एथेनॉल बना देती है|
(iv) प्रक्रिया – साबुनीकरण
}
9113323460

I hope you like it. If you like then please share it and you can also Donate to our website by my number and QR code which is given above.
Thanks.
